Some 3 billion people in the world live outside the cash economy in the world’s poorest nations. Food security and regular supply are their daily concerns. Chronic malnutrition is a leading cause of death and disease for them. Young children are amongst the most affected. One child every 5-10 seconds dies from undernutrition. Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness for someone every minute. Most people in tropical and subtropical countries are iron deficient.
Our goal is to provide information that enables people to choose the right plant for their environment, to give them stable food production and a greater choice of plants to enrich their diets and improve their nutritional wellbeing.
The plant fact sheets listed in this collection are only a small portion of those available from FPI. Please check your plant inquiries in the ECHO Search and reference the FPI plant database for further information.
Most of the plants selected to list here are further described in country-specific publications by Food Plant Solutions (FPS in the Search).
8000 Starchy Staples
7000 Legumes
6000 Leafy Greens
5000 Fruits
4000 Vegetables
3000 Nuts, Seeds, Herbs, and other foods
897 Issues in this Publication (Showing issues - 8000) Previous | Next
Nasturtium officinale
Edible: Leaves, Seeds, Herb, Spice, Vegetable
A cabbage family herb. It is a small leafy plant that grows in water and lasts for several years. It grows 30 cm high and has runners 2.5 m long. It has hollow stems and roots freely from the nodes. It branches freely. The leaves consist of 3 to 7 pairs of small leaflets then a larger leaflet at the end. The flowers are small and white and grow grow in a cluster. Flowers are not always produced and need days with more than 12 hours of sunlight to form. A small narrow curved seed pod about 2 cm long can develop. It grows attached to the banks of streams.
This is a temperate climate crop. It is common in tropical highland creeks especially those flowing off limestone hills. (pH 6.5-7.5) It needs to be in running water. In the tropics it occurs from about 1000 m up to at least 2900 m altitude. It grows in streams, ditches, lakes, swamps, marshes from near sea level to 3700 m altitude in China. In Argentina it grows from sea level to 4,100 m above sea level. It grows in wetlands. It suits plant hardiness zones 6-10. Tasmania Herbarium. In Yunnan. In Sichuan.
Common Names: Acice, Agriaun, Agriao, Awa, Berro, Berro de agua, Berros, Brunnenhresse, Chu-lba-thpu, Chungol, Ciotole, Credou, Creisoun, Creixens, Crescione acquatico, Cresson de fontaine, Dou ban cai, Gerdeme, Gernounej, Gurnounch, Huwaireh, Ip komp, Kalanso, Kambere, Kapisi vai, Kenchi, Kiji, Kizmase, Komba, Kreson, Kuwmba, Kuzala, Kuzele, Lauridde, Lira, Lut-putiah, Mizu garashi, Ok 'oruro, Ota karesi, Pakimbita, Pa nan, Phak nam, Piriya halim, Qije, Sai yeung ts'oi, Salada air, Salada chai, Salade, Sawade, Sayur paret, Selada ayer, Selada sawah, Shimrayo, Shuicai, Silang-sag, Sim rayo, Sim sag, Su teresi, Talib shah, Talmera, Talmira, Tara mira, Tarmera, Taung-kya-gale, Termera, Tharmere, Tujik, Tusmask, Tuzik, Uotakuresu, Waci, Wakari, Xa lach xong, Xi yang cai, Ye qing cai
Synonyms:
Arabis nasturtium Clairv.;
Baeumerta nasturtium P. Gaertn., B. Mey. & Schreb.;
Cardamine aquatica (Garsault) Nieuwl.;
Cardamine fontana Lam.;
Cardamine nasturtium-aquaticum (L.) Borbas;
Nasturtium nasturtium-aquaticum (L.) H. Karst., nom. inval.;
Nasturtium officinale R. Br.;
Radicula nasturtium Cav., nom. illeg.;
Radicula nasturtium-aquaticum (L.) Rendle & Britten;
Rorippa nasturtium Beck, nom. illeg.;
Rorippa nasturtium-aquaticum (L.) Hayek;
Rorippa officinale (R. Br.) P. Royen;
Sisymbrium nasturtium Thunb., nom. illeg.;
Sisymbrium nasturtium-aquaticum L.;
Nelumbo nucifera
Edible: Seeds, Root, Tuber, Leaves, Stamens, Rhizomes, Seeds - coffee, Vegetable, Fruit, Flowers, Tea
A herb which grows in water and continues growing for several years. The rootstock is under water and creeping. The leaf stalk grows 1-2 m high. The leaves can be 20-90 cm across. It has large round leaves which stand out of the water. The stalk joins to the centre of the leaf. It has large attractive pink, red or white flowers which stand out of the water on long stalks. Flowers are pink or white and 15 to 25 cm across. The flower stalk can be longer than the leaf stalk. The mature fruit is a spongy cone shaped structure with several seeds about 1 cm across under the holes in the top. These fruit can be 7-15 cm long. The edible rhizome is submerge in mud.
It is a tropical plant but will grow in cooler places. It needs 20-30°C. It needs full sunshine. It can grow in deep water. It does best in fresh water. The pH can range from 5.6-7.5. It grows in wetlands. It is common in some parts of the Philippines such as Laguna de bay. It is also reported from Camarines, Mindoro, Cotabato and Davao. It will probably grow up to about 1000 m altitude. It occurs in the Fly and Sepik River areas in Papua New Guinea. It is cultivated in most of China except the very northern areas. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 9-12. In XTBG Yunnan.
Common Names: Ambal, Ambuj, Ambuja, Aravinda, Baino, Bhen, Bhishi chya biya, Bhisikandda, Bua-luang, Bua-sai, Bunga padam, Bunga telpok, Chhouk, Chinese lotus, Dhala padma, Dhepra, Erra-tamara, Furong, Hasu, He flower, Hehua, He ye, Indijski lotos, Kalung, Kamal-kakri, Kamal, Kamala, Kankadi, Kanwal, Kokomba, Lian, Lin ngau, Lin, Loto, Lotosblume, Lotus cina, Nadroo, Nelum, Nelumbo, Nelun-ala, Ngau, Padam, Padda, Padda bihar, Padema, Padma, Padon-ma-kya, Padum, Pamposh, Pankaja, Parani baha, Pavan, Pink lotus-lily, Padda phul, Poddo gota, Podum, Purni punp, Renkon, Sacred Lotus lily, Salkub sanga, Salukid ba, Sen, Senthamara, Seroja, Sivapputamarai, Soh-lapudong, Suriyakamal, Tamburu, Tabare beru, Tavare beru, Tavaregadde, Teratai, Thamara, Thamarai, Thambal, Thambou, Thamou, Upal ba, Yavanti, Yeonkkot
Synonyms: Nelumbo caspica Eichw.;
Nelumbo komarovii Grossheim;
Nelumbo nelumbo (L.) Druce, nom. inval.;
Nelumbo nucifera var. macrorhizomata Nakai;
Nelumbo speciosum Willd., nom. illeg.;
Nelumbium speciosum Willd.;
Nymphaea nelumbo L.;
Nelumbium nelumbo (L.) Druce;
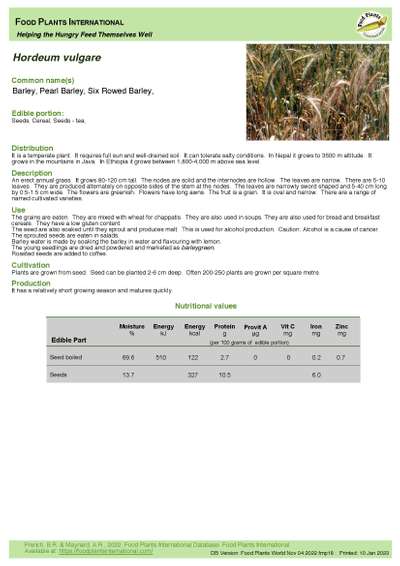
Hordeum vulgare - Barley
Edible Portion: Seeds, Cereal, Seeds - Tea
An erect annual grass. It grows 80-120 cm tall. The nodes are solid and the internodes are hollow. The leaves are narrow. There are 5-10 leaves. They are produced alternately on opposite sides of the stem at the nodes. The leaves are narrowly sword shaped and 5-40 cm long by 0.5-1.5 cm wide. The flowers are greenish. Flowers have long awns. The fruit is a grain. It is oval and narrow. There are a range of named cultivated varieties.
Ipomoea batatas - Sweet Potato
Edible Portion: Tuber, Root, Leaves, Vegetable
This is a root crop which produces long creeping vines. The leaves are carried singly along the vine. Leaves can vary considerably from divided like fingers on a hand to being entire and rounded or heart shaped. At the end of the vine, trumpet shaped flowers grow. They are purple. Under the ground fattened tubers are produced. There are a large number of varieties which vary in leaf shape and colour, tuber shape, colour, texture and in several other ways.
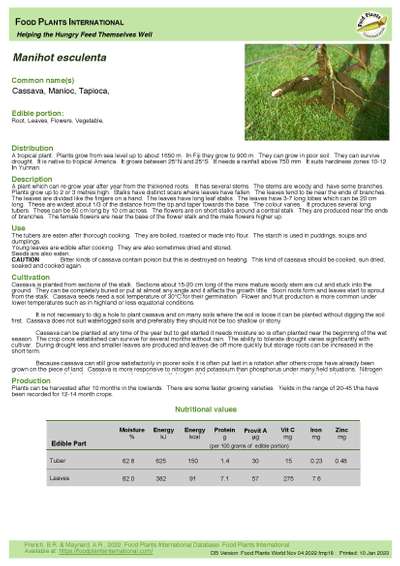
Manihot esculenta - Cassava
Edible Portion: Root, Leaves, Flowers, Vegetable
A plant which can re-grow year after year from the thickened roots. It has several stems. The stems are woody and have some branches. Plants grow up to 2 or 3 metres high. Stalks have distinct scars where leaves have fallen. The leaves tend to be near the ends of branches. The leaves are divided like the fingers on a hand. The leaves have long leaf stalks. The leaves have 3-7 long lobes which can be 20 cm long. These are widest about 1/3 of the distance from the tip and taper towards the base. The colour varies. It produces several long tubers. These can be 50 cm long by 10 cm across. The flowers are on short stalks around a central stalk. They are produced near the ends of branches. The female flowers are near the base of the flower stalk and the male flowers higher up.
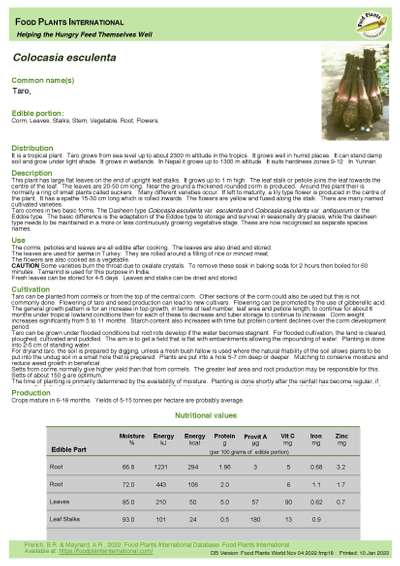
Colocasia esculenta - Taro
Edible Portion: Corm, Leaves, Stalks, Vegetable, Root, Flowers
This plant has large flat leaves on the end of upright leaf stalks. It grows up to 1 m high. The leaf stalk or petiole joins the leaf towards the centre of the leaf. The leaves are 20-50 cm long. Near the ground a thickened rounded corm is produced. Around this plant their is normally a ring of small plants called suckers. Many different varieties occur. If left to maturity, a lily type flower is produced in the centre of the plant. It has a spathe 15-30 cm long which is rolled inwards. The flowers are yellow and fused along the stalk. There are many named cultivated varieties.
Taro comes in two basic forms. The Dasheen type Colocasia esculenta var. esculenta and Colocasia esculenta var. antiquorum or the Eddoe type. The basic difference is the adaptation of the Eddoe type to storage and survival in seasonally dry places, while the dasheen type needs to be maintained in a more or less continuously growing vegetative stage. These are now recognised as separate species names.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius - Elephant Foot Yam
Edible Portion: Tuber, Roots, Corm, Leaves, Leaf Stalks, Vegetable
A taro family plant but with a very divided leaf. It grows to 0.75-1 m high. It is a herbaceous plant with rough and mottled leaf stalks. It has a straight stem and the leaf is divided into leaflets. The leaves can be 1 m in width. The leaves usually come singly from the ground. The leaf blades are divided into many lobes. The leaflets can be 3-35 cm long and 2-13 cm wide. The flower stalk can be 3-20 cm long. The bract around the flower is bell shaped and fluted. It can be 60 cm across. The edge is curved back and wavy. The flower is dull purple and up to 30 cm across. It can be 70 cm long. The flower gives of a bad smell like rotting meat and this attracts flies. The flower only develops after the leaves have died off. The leaves and corms especially in the wild varieties contain many stinging crystals. Edible kinds have a smooth petiole. It has a large round tuber up to 25 cm across. The large round underground corm produces small corms around the side. These can be 10 cm long. These are usually used for planting.
Asparagus racemosus - Climbing Asparagus
Edible Portion: Root, Tubers, Shoots, Fruit, Leaves, Vegetable, Leaves - Tea, Flower
A creeping or climbing herb or shrub. It has woody stems. It grows 2 m high. It spreads 2 m wide. The stems are slender and trailing. The leaves are light green and narrow. They are 5 cm long. The flowers are very small. The fruit are small round red berries.
Guizotia abyssinica - Niger Seed
Edible Portion: Seeds, Leaves, Oil, Vegetable
An erect branched herb. It grows 30-180 cm tall. The stems are soft and hairy. The leaves are usually carried opposite one another. The leaves do not have stalks and they clasp the stem. The leaves have teeth along the edge and the surface is a little rough. The flower head is made up of many small flowers each capable of producing a seed. The fruit (called seeds) are black angled structures. They are up to 12 mm long. The seed inside is 3.5-5 mm long. There are about 250-300 seeds per gram.
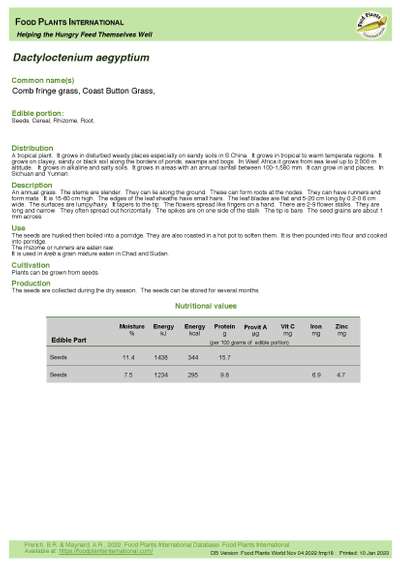
Dactyloctenium aegyptium - Comb Fringe Grass
Edible Portion: Seeds, Cereal, Rhizome, Root
An annual grass. The stems are slender. They can lie along the ground. These can form roots at the nodes. They can have runners and form mats. It is 15-60 cm high. The edges of the leaf sheaths have small hairs. The leaf blades are flat and 5-20 cm long by 0.2-0.6 cm wide. The surfaces are lumpy/hairy. It tapers to the tip. The flowers spread like fingers on a hand. There are 2-9 flower stalks. They are long and narrow. They often spread out horizontally. The spikes are on one side of the stalk. The tip is bare. The seed grains are about 1 mm across.