Some 3 billion people in the world live outside the cash economy in the world’s poorest nations. Food security and regular supply are their daily concerns. Chronic malnutrition is a leading cause of death and disease for them. Young children are amongst the most affected. One child every 5-10 seconds dies from undernutrition. Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness for someone every minute. Most people in tropical and subtropical countries are iron deficient.
Our goal is to provide information that enables people to choose the right plant for their environment, to give them stable food production and a greater choice of plants to enrich their diets and improve their nutritional wellbeing.
The plant fact sheets listed in this collection are only a small portion of those available from FPI. Please check your plant inquiries in the ECHO Search and reference the FPI plant database for further information.
Most of the plants selected to list here are further described in country-specific publications by Food Plant Solutions (FPS in the Search).
8000 Starchy Staples
7000 Legumes
6000 Leafy Greens
5000 Fruits
4000 Vegetables
3000 Nuts, Seeds, Herbs, and other foods
922 Issues in this Publication (Showing issues - 8000) Previous | Next
Phaseolus vulgaris
Edible: Pods, Seeds, Leaves, Vegetable
This bean has very many varieties and varies a lot in details. Both short and climbing cultivated varieties of this bean occur. It has a long taproot. Climbing forms can be 2-3 m tall. Bush types are 20-60 cm tall. The leaves are carried one after another along the stem and the leaves have 3 leaflets. The leaf stalk has a groove on the top. The side leaflets are asymmetrical in shape. The leaflets can be 8-15 cm by 5-10 cm. The flowers are in the axils of leaves and have few flowers in a loose form. Flowers are white to purple and pods smooth. Pods are slender and 8-20 cm long by 1-1.5 cm wide. The pods are straight or slightly curved and with a beak at the end. Pods often have 10-12 seeds which are kidney shaped and coloured. There are more than 500 cultivated varieties.
A temperate plant. It mostly grows from 700 m to 2000 m altitude in the tropics. In the lowlands it suffers from pest and disease but it can be grown to sea level. It is not suited to the wet tropics. It is shallow rooted and therefore damaged by excess moisture near the roots. About 350 mm of water is enough for a crop life cycle. It is sensitive to frost and to high temperatures. Flowers will not form below 9.5°C and night temperatures above 37°C cause flowers to drop. The best temperature is 15-21°C. It does not suit very acid soils. In Nepal it grows up to 1200 m altitude. It suits hardiness zones 8-11.
Common Names: Affi, Alatram, Asare simi, Ashlan bu'ul, Babri, Bakia, Bakla, Barigalu, Binisi, Black beans, Bonchi, Bo-sa-pe, Buli, Cannellini bean, Chiclayo, Ebihimba, Ebijanjaalo, Ebikanga, Ebisobooza, Ebisobyo, Ejote, Fagiolo, Fasiole, Feijao-preto, Frash bean, French bean, Frijol, Green bean, Habi cheulas, Haricot bean, Hto-pe-ton, Ingem mame, Ingen mame, Judia, Kacang buncis, Kachang bunchis, Kachang pendek, Kidney bean, Lobia, Mahalagi, Makasikila, Malemba, Marakwa, Mattu wanyambi, Mete-beir, Mulu fintsumu, Navy bean, Ngaingai, Ngor, Noviya, Nyemba, Phanasi, Pini, Pinto beans, Poroto, Po to sa, Pra-say-taut, Purutu, Rajama, Rajmah, Rajma sibi, Sanndaek barang, Shravanghevda, Snijboon, Stapu, Ta-la-pe, Te bin, Teiko, Thia khaek, Tingalavari, To-tok, Tsai douk, Tsaramaso, Turtle bean, Wamolo
Synonyms:
Phaseolus compressus DC.;
Phaseolus compressus var. carneus G. Martens;
Phaseolus compressus var. cervinus G. Martens;
Phaseolus compressus var. ferrugineus G. Martens;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. albus G. Martens;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. aureolus G. Martens;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. helvolus Savi;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. mesomelos Haberle;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. pictus Caval.;
Phaseolus ellipticus var. spadiceus G. Martens;
Phaseolus gonospermus var. oryzoides G. Martens;
Phaseolus gonospermus var. variegatus Savi;
Phaseolus nanus Linn.
Phaseolus oblongus var. albus G. Martens;
Phaseolus oblongus var. spadiceus Savi;
Phaseolus oblongus var. zebrinus G. Martens;
Phaseolus sphaericus var. atropurpureus G. Martens;
Phaseolus sphaericus var. minor G. Martens;
Phaseolus vulgaris var. albus Haberle;
Phaseolus vulgaris var. nanus G. Martens;
Phaseolus vulgaris var. niger G. Martens;
Phaseolus vulgaris var. ochraceus Savi;
Phaseolus vulgaris var. variegatus DC.;
Phaseolus zebra var. carneus G. Martens;
Phaseolus zebra var. purpurascens G. Martens;
Petroselinum crispum
Edible: Leaves, Herb, Spice, Vegetable, Seeds
A short lived perennial plant. Often it grows and flowers over two years. It forms clumps and is a hairless plant. It has stems up to 50 cm long which are upright and with grooves. They branch. Several stems come from the top of the fattened taproot. It spreads to 50 cm across. The leaflets are finely divided. They are feather like and dark green. They are triangular and divided 3 times. They are divided into toothed segments about 3 cm long. They have a strong smell. The flowers are greenish white and star shaped. They occur at the ends of branches. The flowers are flat topped and up to 4 cm across. There are about 30 variations of curled parsley. Some are more tightly curled than others.
Wild parsley also occurs in some temperate places. It can be cooked and eaten.
A temperate plant. It can be grown from sea level up to 2400 m altitude in the tropics. It grows best in moderately cool, shady and humid conditions. It can grow well in full sunlight but also in slight shade. Young plants can be damaged by frost. It is best with a pH of 5.0-6.0. It suits hardiness zones 7-9.
Common Names: Achu mooda, Faan uen sai, Fan yan sui, Julivert, Maydanoz, Okhrakhushi, Patraseli, Peregil, Perejil, Persil, Persille, Petersilie, Pletik apu, Potrasoli, Pravi peteršilj, Prezzemolo, Salsa, Salsinha
Synonyms: Apium crispum Mill.;
Apium petroselinum L.;
Petroselinum hortense Hoffm.;
Petroselinum sativum Hoffm.;
Petroselinum vulgare Lag.;
Crispum petroselinum;
and others
Phaseolus coccineus
Edible: Seeds, Pods, Leaves, Roots, Vegetable, Flowers
A climbing bean. It is a robust plant and keeps growing from year to year by re-growing from the fattened root. The stems are often hairy. It grows 1.8-2.4 m high. It can spread 1.8-2.4 m wide. It twines around a trellis. The leaves are compound and have three leaflets. The flowers are bright red. They are in clusters 2.5 cm long. The pods are long (30 cm) and with a wavy edge. The seeds are large and can be several different colours. It sometimes has a root tuber.
A tropical plant. It grows naturally in the mountain regions from Mexico to Panama. It is grown in the highlands in the tropics. On the tropical coast seedlings die and pods are not formed. It is damaged by frost. It suits hardiness zones 8-10. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
Common Names: Ayacote, Botil, Chamborote, Chilipuca, Climat, Cub, Cubaces, Dau son, Dutch caseknipe bean, Ejote, Fagioli rampicante di Spagna, Frejol de castilla, Frejol de monte, Frijol chamborote, Hana mame, Haricot d'Espagne, Kacang besar, Koto moruk, Laški fižol, Patol, Poroto chileno, Seven year bean, Shim
Synonyms:
Phaseolus multiflorus Willd.;
Phaseolus coccineus var. zongolicensis Freytag, nom. inval.;
Phaseolus multiflorus Lam.;
Phaseolus lunatus
Edible: Seeds, Leaves, Pods, Vegetable, Flowers
A perennial climbing bean. It is often a tall vigorously climbing plant which can keep growing for some years. The leaves are slightly rounded at the base and pointed at the tip. The flower is white or yellow. The keel of the flower is twisted which helps tell the difference between this bean and Lablab bean. The pods are long (10 cm), flattened and curved and have 3-4 seeds which are very variable in colour. The seeds are large. The seeds have a short round hilum where the seed is attached to the pod. The seeds also have lines going out from this point across the bean seed.
It suits warm and subtropical areas. In the tropics it is common between 500 and 2100 m altitude but grows to the limit of cultivation (2700 m). For germination it must have a soil temperature above 15.5°C and cannot withstand frost. In very hot weather seeds often do not set. It does best in a temperature range 14-21°C. It is sensitive to a pH less than 6. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 8-11. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Abongband, Agwa, Akbaka, Akpatramo, Amaijalero, Apteram, Awuje, Behna, Beloi, Butter bean, Civet bean, Ckuku, Daful, Dau bach-bien, Dau-diem, Dau-ngu, Ebigaaga, Ewuje, Feijao-magalo, Frejol de manteca, Frijol caballero, Haba, Haba pallar, Habilla, Htawbat-pe, Kachang china, Kachang jawa, Kachang mas, Kachang serendeng, Kal-beir-kan, Kara, Kawl-be, Kekara, Khasi kollu, Korokoco, Kpokpo, Kratok, Limski fižol, Lobia, Lobiya, Muma kedeba, Obuhindhini, Obuyindiyindi, Okuku, Onguk, Orusa, Patani, Pe-bra, Pe-byu-gyi, Pe-gya, Roway, Santagu-pe, Sem, Sieva Bean, Taipee, Tim-sin, Torta, Tua rachamat, Tunoran, Wake
Synonyms:
Phaseolus bipunctatus Jacq.;
Phaseolus inamoenus L.;
Phaseolus limensis Macfad.;
Phaseolus lunatus var. macrocarpus Benth.;
Phaseolus portoricensis Sprengel;
Phaseolus puberulus Kunth;
Phaseolus saccharatus Macfad.;
Phaseolus tonkinensis Lour.;
Phaseolus zuaresii Zuccagni;
Persicaria chinensis
Edible: Leaves, Seeds, Leaves - tea, Flowers, Fruit
A herb. It is a straggling perennial weed often woody near the base and up to 2-3 m tall. It can be a climber. Branches are ridged and grooved. Leaves are alternate and have stalks. The leaves are 2.5-14 cm long by 1.3-8 cm wide. They are oblong to sword shaped. They taper to the tip. They are hairy on the mid vein underneath. The base is cut off. Flowers are at the top and are white or pink. A black berry-like fruit develops with a 3 sided shape.
A tropical and subtropical plant. In Nepal it grows between 700-2200 m altitude. It grows in moist, open places. It grows in wetlands. It occurs in natural forest clearings and in abandoned gardens. It is mostly between 1000 m and 2500 m altitude. It occurs in the Western Ghats in India. In XTBG Yunnan.
Common Names: Ameta, Angom-yensil, Bai fan teng, Bai-vu, Bakhre thotne, Behu, Beng gen, Besongali, Bilichini, Boktaung, Chorakam, Delap, Duoi tom, Ganigalu, Gelaiche, Heganturia, Ja-lynnong, Jampera, Kaker bantabhat, Kakka karumbu, Kakur thotne, Kelnap, Kolemukku dagu, Kuki, Kukur thotne, Kundyut-pam, La lom, Lorum, Lymbeh, Madhu soleng, Madhuri tenga, Maha-gar-kyan-sit, Maikhri thai, Mekri donok, Modhu soleng, Mohicharan sak, Narali, Obei-o kati, Obiovu, Okhi morokpo, Okung, Paral, Phiahapa, Pokok semuloh, Ratnaulo, Qaub yag, Ta-ham, Theidon, Thom lom, Wetkyein, Yerumai naakku chedi
Synonyms:
Polygonum chinense L.;
Ampelygonum chinense (L.) Lindley;
Coccoloba crispata Buch.-Ham. ex Roxb.;
Polygonum auriculatum Lam.;
Polygonum brachiatum Lam.;
Polygonum patens D.Don;
Persicaria hydropiper
Edible: Leaves, Seeds, Leaves - spice, Leaves - tea
An annual herb. The stems are erect and curve upwards. It can be 80-100 cm tall. The stem has many branches. It forms roots at the nodes. The nodes are enlarged and they have a red ring at the base. The leaves are alternate and narrowly sword shaped. They have glands. The leaves narrow towards their base. The leaves have a peppery taste when chewed. There is a stipule or leaf like structures at the base of the leaf stalk. This has bristles. The leaf stalk is 2-5 mm long. The blade is sword shaped and 2-8 cm long by 0.5-2 cm wide. The flowers are in a slender spike. The spike is spread along the stalk. It tends to bend over. The flowering shoots can be 17 cm long. The individual flowers are small and white. There are 2 subspecies suited to temperate and tropical locations.
It is a temperate plant. It grows in shallow water along the edges of creeks and rivers. It grows in wetlands. It grows in open waste places. It suits sunny wet locations. It can grow from the seashore to 1500 m altitude. Tasmania Herbarium. In Yunnan. In Sichuan.
Common Names: Agagat, An ji ba qian, Behu, Bislangi, Buding, Cacabean, Chaokhong, Common smartweed, Daun senahun, Ganeri, Ngh(eer) n(uw)(ows)c, Ngh(eer) r(aw)m, Numshim-muk, Packur mul, Pani-maricha, Papreni lisac, Pha chi mi, Phak phai nam, Pungent smartweed, Ram-nuoc, Ratnaulo, Rumput tuboh, Si tuba sawah, Smartweed, Tade, Tuba, Tube seluwang, Water pepper, Yanagi-tade
Synonyms:
Persicaria acris Gilib.;
Persicaria hydropiper (L.) Opiz;
Persicaria hydropiper (L.) Spach;
Persicaria vernalis Nakai;
Peutalis hydropiper Raf.;
Polygonum hecasanthum Schur;
Polygonum hydropiper L.;
Polygonum koreense Nakai;
Polygonum obtusifolium Schur;
Polygonum oleraceum Schur.;
Polygonum shinzii J. Schust.;
Persicaria odorata
Edible: Leaves, Herb
A leafy creeping plant which continues to grow from year to year. It forms roots at the nodes. The stems are reddish and have joints where the leaves join. These are 1-5 cm apart. The stems can be 35 cm high. The leaves are 5-8 cm long and sword shaped. They are green in colour with brown or red marks on the top surface. The flowers are small and pink and are produced at the end of the stems.
A warm temperate to subtropical plant. It does well with lots of water. It can grow under shady conditions. It can grow in heavy soil. It can be grown in pots and hanging baskets. It suits warm or tropical conditions and cannot survive frost. It needs fertile well drained soil. It suits hardiness zones 8-10.
Common Names: Amadokoro, Asian mint, Cambodian mint, Chan chom, Chi krasang tomhom, Coriandre du Vietnam, Daun kesom, Daun kesum, Daun laksa, Hom chan, Hot mint, Knotweed, La liao, Laksa Blatt, Laksa leaf, Paew, Pakpai, Phak phai, Phak pheo, Phrik maa, Phud phaeng, Rau Ram, Rau ram, Vietnamese coriander
Synonyms:
Polygonum odoratum Lour.;
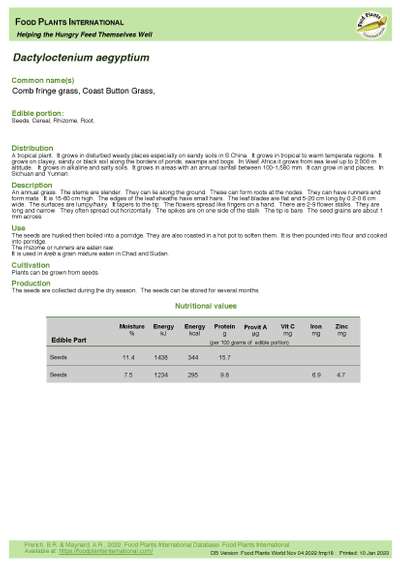
Dactyloctenium aegyptium - Comb Fringe Grass
Edible Portion: Seeds, Cereal, Rhizome, Root
An annual grass. The stems are slender. They can lie along the ground. These can form roots at the nodes. They can have runners and form mats. It is 15-60 cm high. The edges of the leaf sheaths have small hairs. The leaf blades are flat and 5-20 cm long by 0.2-0.6 cm wide. The surfaces are lumpy/hairy. It tapers to the tip. The flowers spread like fingers on a hand. There are 2-9 flower stalks. They are long and narrow. They often spread out horizontally. The spikes are on one side of the stalk. The tip is bare. The seed grains are about 1 mm across.
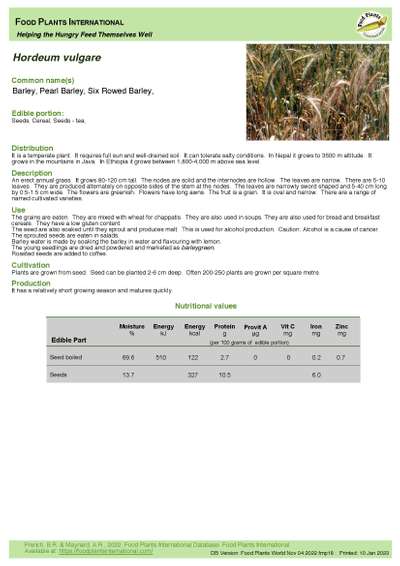
Hordeum vulgare - Barley
Edible Portion: Seeds, Cereal, Seeds - Tea
An erect annual grass. It grows 80-120 cm tall. The nodes are solid and the internodes are hollow. The leaves are narrow. There are 5-10 leaves. They are produced alternately on opposite sides of the stem at the nodes. The leaves are narrowly sword shaped and 5-40 cm long by 0.5-1.5 cm wide. The flowers are greenish. Flowers have long awns. The fruit is a grain. It is oval and narrow. There are a range of named cultivated varieties.
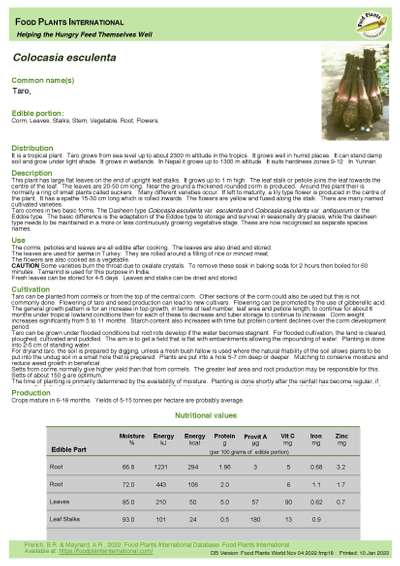
Colocasia esculenta - Taro
Edible Portion: Corm, Leaves, Stalks, Vegetable, Root, Flowers
This plant has large flat leaves on the end of upright leaf stalks. It grows up to 1 m high. The leaf stalk or petiole joins the leaf towards the centre of the leaf. The leaves are 20-50 cm long. Near the ground a thickened rounded corm is produced. Around this plant their is normally a ring of small plants called suckers. Many different varieties occur. If left to maturity, a lily type flower is produced in the centre of the plant. It has a spathe 15-30 cm long which is rolled inwards. The flowers are yellow and fused along the stalk. There are many named cultivated varieties.
Taro comes in two basic forms. The Dasheen type Colocasia esculenta var. esculenta and Colocasia esculenta var. antiquorum or the Eddoe type. The basic difference is the adaptation of the Eddoe type to storage and survival in seasonally dry places, while the dasheen type needs to be maintained in a more or less continuously growing vegetative stage. These are now recognised as separate species names.