Edible: Leaves, Fruit, Vegetable, Flowers
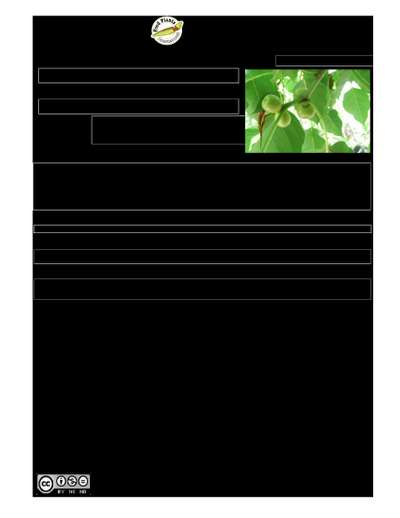
A fig. It is a tree. It grows about 15 m tall. Usually it lives growing on and attached to other trees. The bark is grey and wrinkled when dry. The leafy growth at the base of the leaf is oval and 1.2-2.5 cm long. It leaves a scar which is easy to see. The leaf stalk is 6-8 cm long. The leaf blade is heart shaped or oval and 6-13 cm long by 6-11 cm wide. It is somewhat leathery. The base is broadly wedge shaped and it tapers to the tip. There are 4 veins near the base then 5-6 secondary veins on each side of the main vein. Normally there are a pair of figs in the axils of leaves. Sometimes they are in groups on older leafless branches. They have dark spots when young. They are dark purple when mature. They are round and without stalks. They are 1-1.5 cm across. There are only a few male flowers scattered amongst the other flowers.
A tropical plant. In China it grows along trails between 600-700 m altitude in Yunnan.
Common Names: False Buddha tree, Asht, Bettaarali, Dumur, Gagjaira, Gaiaswat, Gai aswathwa, Gajna, Hay, Jakri, Jia putishu, Kabar, Kathepipal, Mawnglae, Mawnglaw, Mawnglok, Paharepipal, Pair, Pakar, Pakur, Payar, Pilkhan, Prap, Wagrans, Xin ye rong
Synonyms:
Ficus cordifolia Roxb.;
Ficus conciliorum Oken;
Ficus damit Gagnep.;
Urostigma cordifolium (Roxb.) Miq.;
Urostigma rumphii (Blume) Miquel;