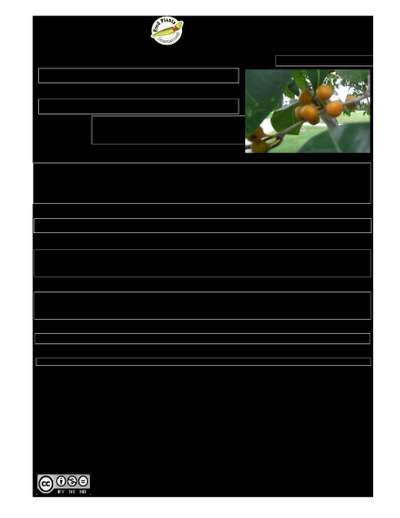
Edible: Fruit, Leaves
A fig. It is a small tree or shrub 2-4 m high. It can climb and scramble over other plants and be up to 10 m high. The small branches are rough. The small branchlets are yellow or pale brown. The bark is grey or brown and cracked or flaky. The leafy structure at the base of the leaves is sword shaped and 5-10 mm long and thick. The leaves of the tree are yellowish with purple veins and short leaf stalks. The leaves are 4-13 cm long and 2-6 cm wide. The leaf stalk is 0.6-1 cm long. Male and female flowers occur on separate plants. The figs are in the leaf axils and up to 2 cm across and orange coloured. There are some varieties described based on the size of the plant and the size of the figs.
A tropical plant. Trees are common on limestone or coral rocks near the sea shore. It tends to be on coral soils. In the Pacific it grows from sea level to 750 m altitude.
Common Names: Dye fig, Awal, Awan, Awann, Awen, Coain, Felo, Gawal, Guwan, Gawann, Hawan, Hmei-thai-thei, Hoda, Hodda, Hotda, Howel, Kiro kesik, Mai-hai-sa-pye, Mati, Mok, Nihn, Nin, Nunu, Nyaung-thabye, Oseked, Oseched, Savirewa, Srah, Tagete, Topdo, Te bero, Topodo, 'U'apea, Wach'guy, Wachaguy, Xie ye rong
Synonyms:
Ficus chlorosykon Rechinger;
Ficus validinervis Benth.