Description

These stoves are useful in areas where sawdust is a readily available waste product. The sawdust or other fuel is packed into a brick frame or can frame and will burn fairly clean with little smoke. These stoves can bring one gallon of water to a boil in approximately 12 to 15 minutes and will maintain an intense temperature for two to five hours, depending on the fuel used and the compression of the fuel (fine, highly compressed sawdust burns longer than coarse or loose material). In addition to sawdust, fibrous plant waste such as rice hulls, chaff, coffee bean hulls and straw can be used as fuel. When using coarser material it is helpful to mix in some sawdust to help hold the fuel together.
Brick Model
 Gather Materials
Gather Materials
- 28 Bricks
- Two pieces of pipe, sticks, or bamboo: 3in (7.5cm) diameter and 2ft (0.6 m) length
- Sawdust, rice hulls or other fuel
How-to
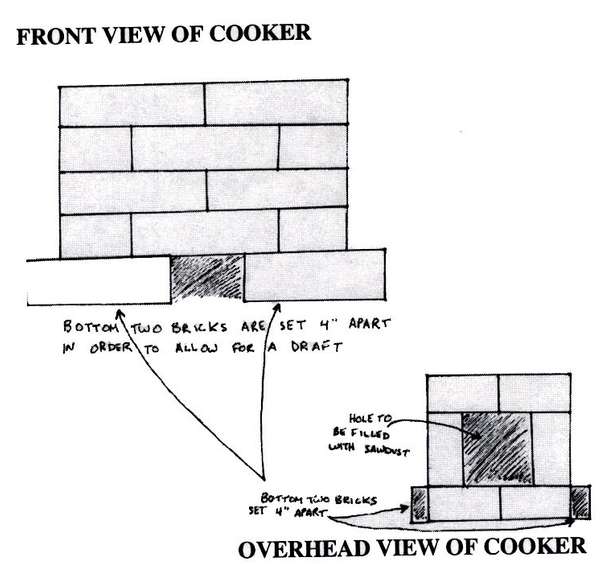
Use 28 bricks (or more if you want a bigger cookstove) and stack them so that they form an enclosure that is 5 bricks high (12 inches; 30 cm) and 2 bricks wide (16 inches; 40 cm).
On the front side of the stove set the bottom two bricks about 4 inches (10 cm) apart from each other. This opening will serve to create a draft.
Now slide one piece of pipe into the opening at the front of the stove. Insert the other piece of pipe into the top of the stove so that it meets the first piece at a right angle.
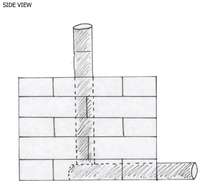
 The vertical pipe must be held in place while sawdust is poured into the top of the stove. As the sawdust is added, it must be packed tight with a tamp. Fill the stove all the way to the top and continue to tamp the sawdust. This stove is able to hold about 5 gallons (19 litres) of sawdust. Once the stove is full the vertical pipe should stand straight up under the support of the sawdust. At this time the vertical pipe can be slowly removed. The best way to get the pipe out is to slowly twist it as you pull it straight up and out of the sawdust. As the pipe exits the sawdust, it should leave a tunnel behind. Now slowly remove the front pipe in the same fashion.
The vertical pipe must be held in place while sawdust is poured into the top of the stove. As the sawdust is added, it must be packed tight with a tamp. Fill the stove all the way to the top and continue to tamp the sawdust. This stove is able to hold about 5 gallons (19 litres) of sawdust. Once the stove is full the vertical pipe should stand straight up under the support of the sawdust. At this time the vertical pipe can be slowly removed. The best way to get the pipe out is to slowly twist it as you pull it straight up and out of the sawdust. As the pipe exits the sawdust, it should leave a tunnel behind. Now slowly remove the front pipe in the same fashion.
 Arrange the top four bricks so that a pot can sit on them and rest directly above the flame. Bricks can be adjusted to form a larger or smaller opening.
Arrange the top four bricks so that a pot can sit on them and rest directly above the flame. Bricks can be adjusted to form a larger or smaller opening.
To start the stove, drop a flaming piece of newspaper (or a match or a coal) down the hole on top. To control the draft, place a brick in front of the opening at the bottom of the stove and slide it to adjust the size of the opening.
It can be useful to place a flat piece of metal with a hole cut in it on top of the sawdust. The metal plate drops down as the sawdust burns and helps to ensure even burning. It also keeps the fuel burning in the center.
 Two Can Model
Two Can Model
Another design for a simple sawdust cooker was described in EDN and can be found in Amaranth to Zai Holes, p. 336.
The stove is made from one large metal can or two smaller metal cans. Remove the tops on both cans. For the top can cut the bottom so that it forms tabs that are bent out and allow it to set into the bottom can. For the bottom can cut a 1.5 in (3.8 cm) hole in the middle of the bottom. Fix the two cans together and insert a metal or PVC pipe or wooden pole vertically in the hole, and add dry sawdust in layers, packing it down firmly before adding more. When the can is full, carefully remove the pipe or pole straight out of the sawdust to form a flue. Twist it slowly as you pull to keep from knocking particles loose. Place the can on two bricks which touch on one corner. Air will enter the bottom hole and be drawn up the flue by the flame. Light some paper and put it under the flue to ignite the sawdust. The sawdust will burn from the red-hot central core outward with an almost invisible flame.
Place two metal pieces across the top of the can on which to set the pot while holding it high enough to maintain a draft for the flame. If you want to set the pot directly on top of the can, you should drill several small holes around the top to allow for air flow. Smoke can be reduced by cutting a 1.5 in hole in the removed lid and placing it on top of the sawdust after packing the stove. To nearly eliminate smoke, cover the outside edges of the lid with a small amount of soil or sand. The lid sinks down as the sawdust burns.
To make the stove burn longer, increase the stove's diameter. Test stoves at ECHO 6 inches in diameter and 8 inches high (15 and 20 cm) burned for three hours, although toward the end the heat was not intense. A stove 16 inches in diameter and 20 inches high (41 and 51 cm) burned for over 8 hours. To make the stove burn hotter, use a taller container or join two cans together.
Regulate the rate of burning by opening or closing the base bricks to modify air flow. It is difficult to extinguish the stove by cutting off the air flow as most fuels continue to smolder until they are completely burned. With some materials, ash will collapse inward and it may be necessary to gently clean out the bottom vent hole to maintain air flow.
Cite this article as:
Dahlman, J. and C. Forst 2001. Sawdust Cookstove. ECHO Technical Note no. 40.