Presented By: Goodluck Malisa
Event: Symposium on Best Practices in Sustainable Agriculture (2019/02/14)
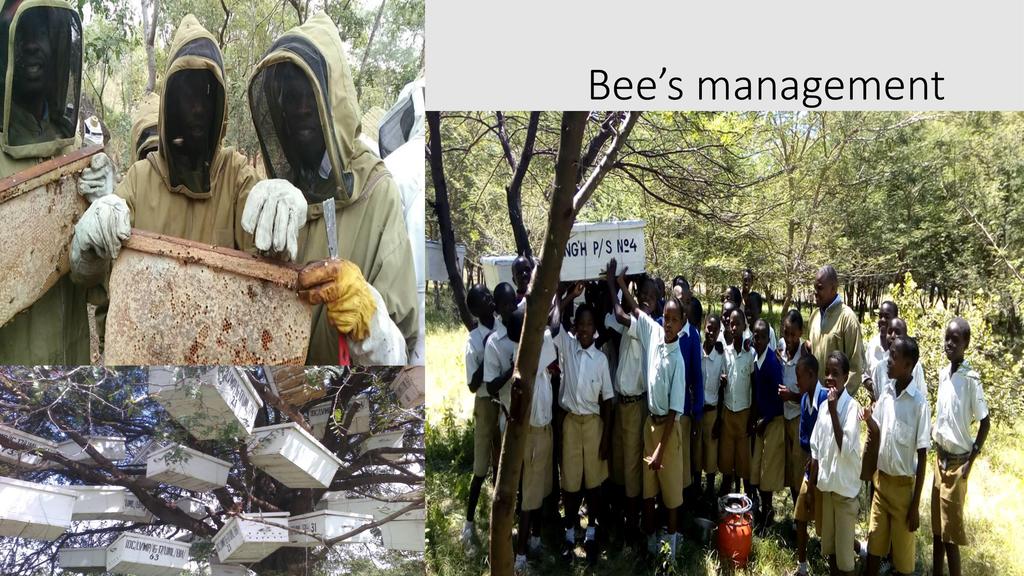
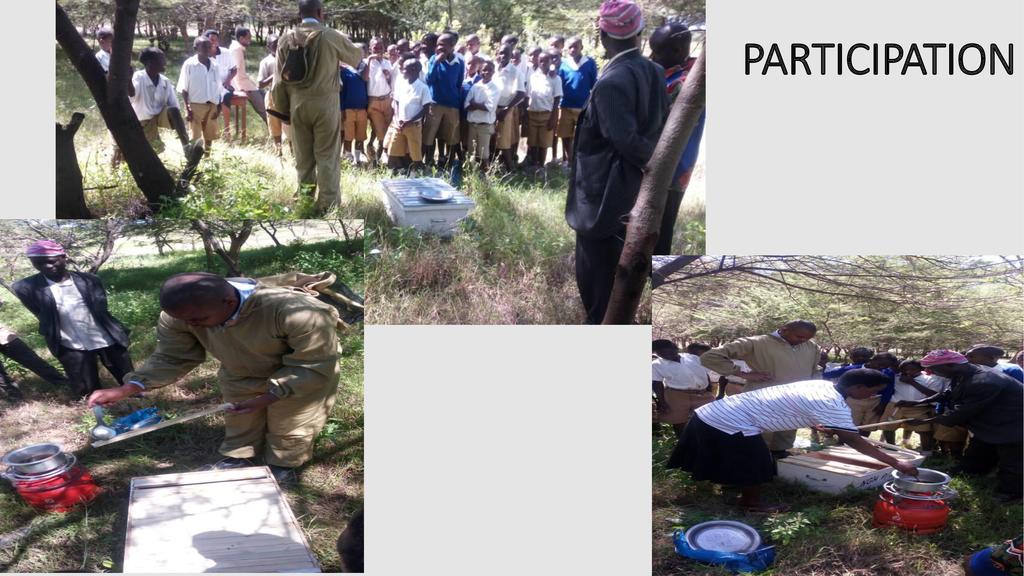
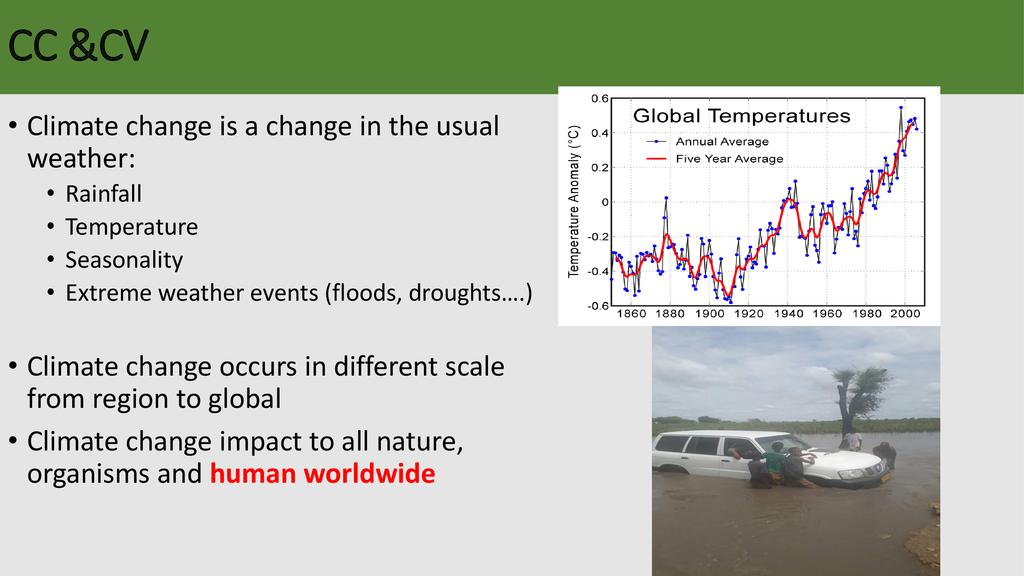
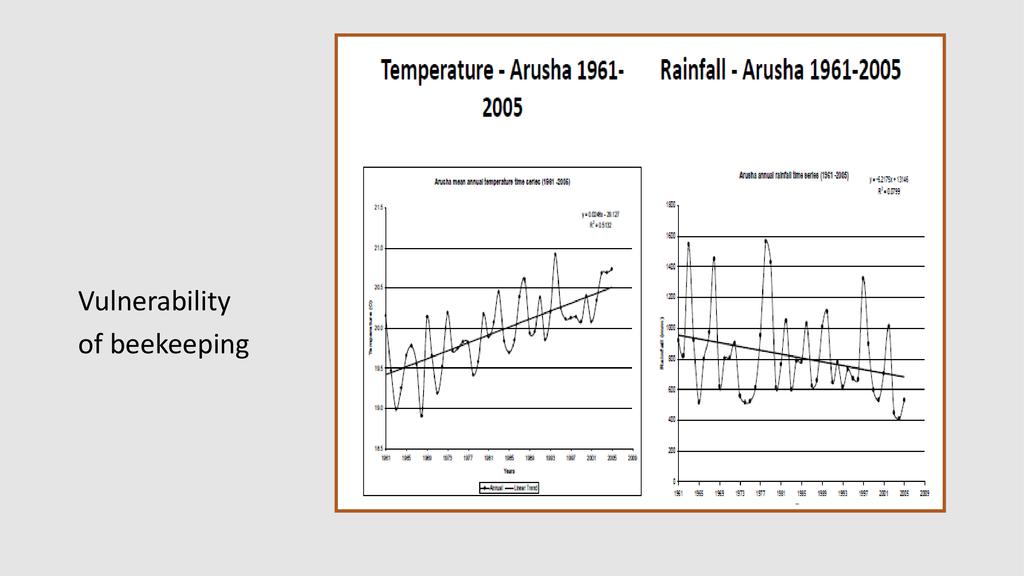
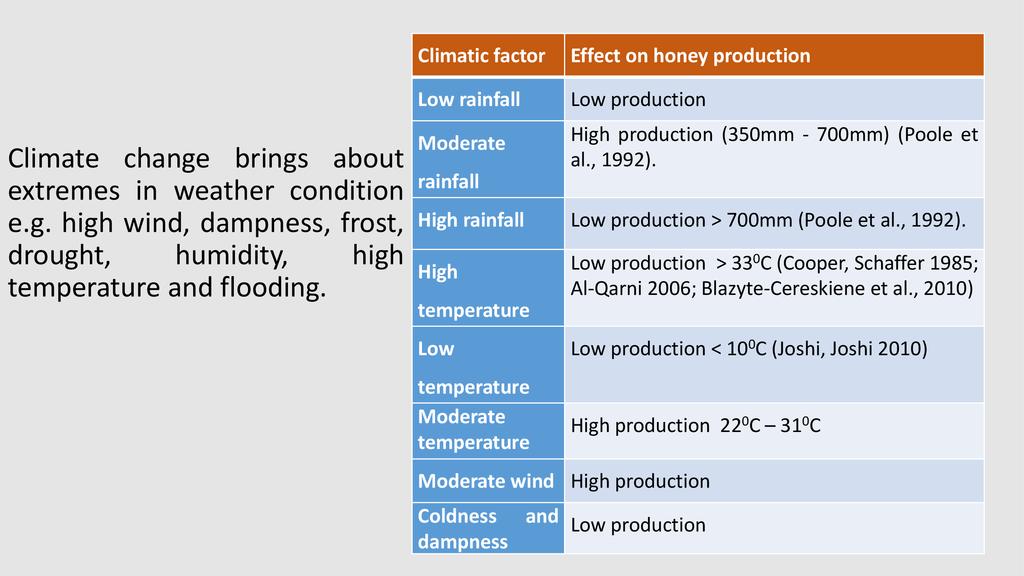
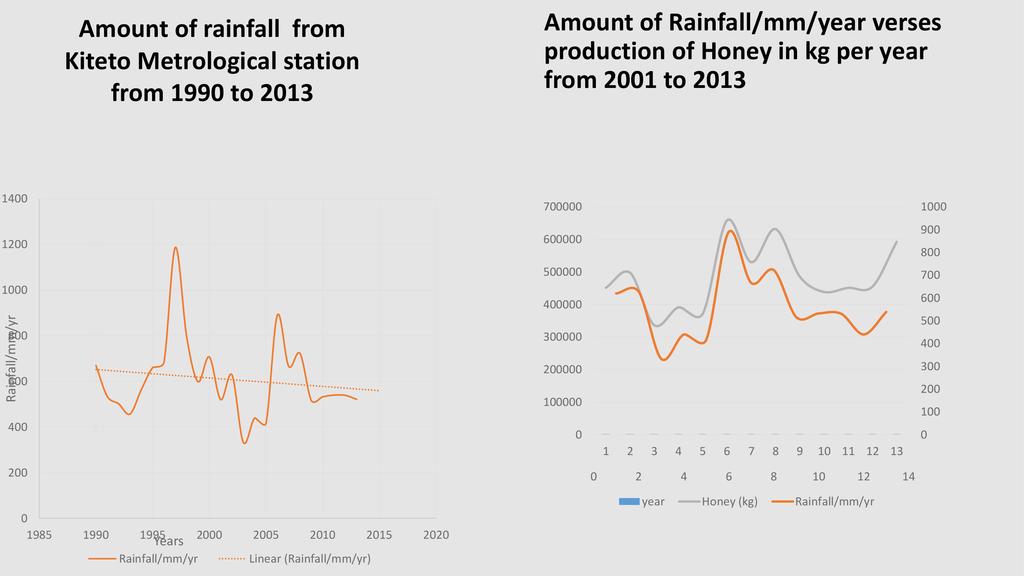
Session: Pollinators are a key component of global biodiversity, providing vital ecosystem services to crops and wild plants. There is clear evidence of recent declines in both wild and domesticated pollinators, and parallel declines in the plants that rely upon them. Here we describe the nature and extent of reported declines, and review the potential drivers of pollinator loss, including habitat loss and fragmentation, agrochemicals, pathogens, alien species, climate change and the interactions between them. Pollinator declines can result in loss of pollination services which have important negative ecological and economic impacts that could significantly affect the maintenance of wild plant diversity, wider ecosystem stability, crop production, food security and human welfare. Food security can therefore be attained through improved crop pollination and generation of extra household income from sales of bee products in most developing countries.
Biographical information: Goodluck Malisa, a PhD student at the University of Dar es Salaam.