Some 3 billion people in the world live outside the cash economy in the world’s poorest nations. Food security and regular supply are their daily concerns. Chronic malnutrition is a leading cause of death and disease for them. Young children are amongst the most affected. One child every 5-10 seconds dies from undernutrition. Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness for someone every minute. Most people in tropical and subtropical countries are iron deficient.
Our goal is to provide information that enables people to choose the right plant for their environment, to give them stable food production and a greater choice of plants to enrich their diets and improve their nutritional wellbeing.
The plant fact sheets listed in this collection are only a small portion of those available from FPI. Please check your plant inquiries in the ECHO Search and reference the FPI plant database for further information.
Most of the plants selected to list here are further described in country-specific publications by Food Plant Solutions (FPS in the Search).
8000 Starchy Staples
7000 Legumes
6000 Leafy Greens
5000 Fruits
4000 Vegetables
3000 Nuts, Seeds, Herbs, and other foods
948 Issues in this Publication (Showing issues - ) Previous | Next
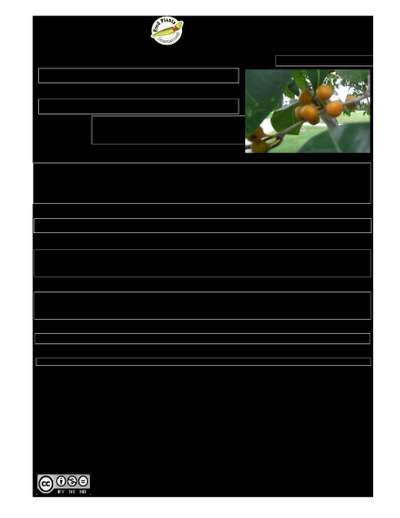
Ficus sycomorus
Edible: Fruit, Leaves, Vegetable, Bark, Gum
A fig. It is a deciduous tree. It grows to 13-25 m high and spreads to 14 m across. It has a rounded crown. The stem is erect. Sometimes the stem has buttresses. The base of the tree commonly spreads over the ground. The bark is yellowish. The leaves are olive green, oval or almost round. They are 5-12 cm long and 3-10 cm wide. The leaves are rough and leathery. They are hairy. The edge of the leaf is wavy and roughly toothed. The leaf stalk is 3 cm long. In dry seasons the tree may lose its leaves. The flowers are 2 cm across and roundish. The fruit are small and edible. They are 3 cm across. They grow in dense clusters in the axils of leaves or on main branches and on the trunk. The fruit are yellow-red when ripe.
A tropical plant. They will grow on most soils. Soils need to be well drained. They prefer a sunny open position. It is drought and frost resistant. It is probably damaged by frost when in leaf. It can grow in hot and arid regions. It grows well near rivers. In Africa trees are commonly near rivers in dry regions. It grows in areas with an annual rainfall between 200-1,800 mm. It can grow in salty soils. It can grow in arid places. It grows in Miombo woodland in Africa. It grows in the Sahel. It suits hardiness zones 10-12.
Common Names: Sycamore fig, Asses fig, Atielowinyo, Bamba, Barde, Bobi, Daray, Ebobore, Ebwalai, Ecalawinyo, Egyptian sycamore, Ejinga, Emidit, Engop, Eta, Figueira-branca, Fuqa, Ganyaya, Gomeiz, Harbu, Hillteta, Ibbi debbi, Ikuku, Ingaboli, Kajare, Kankanga, Katjere, Le'a, Mochaba, Mbuyo, Mkuu, Mkuwa, Mkuyu, Mochaba, Mogoboya, Msoho, Msombe, Mtsombe, Muhuyalukuse, Muhuyuvhuwa, Mukankanwa, Mukuiu, Mukumyu, Mukunyu, Mukuyu, Mulberry fig, Muonde, Mutole, Nkuwa, Nomas, Nshembe, Oda, Odaa, Olam, Ol-gnagboli, Omukwiyu, Orng'aboli, Ourof, Pharoah's fig, Saqam, Saqum, Shafa, Shola, Sou toro, Subula, Suqmi, Sycamore in the Bible, Trosvy, Umkhiwa, Wokoyo, Wola, Wuuri
Synonyms:
Ficus gnaphalocarpa (Miq.) A Rich.;
Ficus damarensis Engl.;
Ficus mucuso Welw. ex Ficalho;
Ficus trachyphylla Fenzl.;
and several others
Ficus tinctoria
Edible: Fruit, Leaves
A fig. It is a small tree or shrub 2-4 m high. It can climb and scramble over other plants and be up to 10 m high. The small branches are rough. The small branchlets are yellow or pale brown. The bark is grey or brown and cracked or flaky. The leafy structure at the base of the leaves is sword shaped and 5-10 mm long and thick. The leaves of the tree are yellowish with purple veins and short leaf stalks. The leaves are 4-13 cm long and 2-6 cm wide. The leaf stalk is 0.6-1 cm long. Male and female flowers occur on separate plants. The figs are in the leaf axils and up to 2 cm across and orange coloured. There are some varieties described based on the size of the plant and the size of the figs.
A tropical plant. Trees are common on limestone or coral rocks near the sea shore. It tends to be on coral soils. In the Pacific it grows from sea level to 750 m altitude.
Common Names: Dye fig, Awal, Awan, Awann, Awen, Coain, Felo, Gawal, Guwan, Gawann, Hawan, Hmei-thai-thei, Hoda, Hodda, Hotda, Howel, Kiro kesik, Mai-hai-sa-pye, Mati, Mok, Nihn, Nin, Nunu, Nyaung-thabye, Oseked, Oseched, Savirewa, Srah, Tagete, Topdo, Te bero, Topodo, 'U'apea, Wach'guy, Wachaguy, Xie ye rong
Synonyms:
Ficus chlorosykon Rechinger;
Ficus validinervis Benth.
Ficus variegata
Edible: Leaves, Fruit, Sap
A fig. It is a medium sized buttressed tree up to 7-18 m high. The trunk varies in length and can be 20-30 cm across. Trees can be larger. The bark is characteristically brown and smooth. It is thick with an abundance of latex. The young shoots are pale green. The leaves are broad and oval and leathery, shiny and smooth. They are 14-20 cm long and 8-12 cm wide. The base of the leaves is rounded and heart shaped. The leaf stalks are 3 to 8 cm long and brown. The leaf like structures (stipules) at the base of the leaf stalks are 1-1.5 cm long, smooth and pinkish. Swollen structures are found along the larger limbs. Red figs with white spots are produced on the trunk and larger branches. The fruit is round and smooth and turns deep yellow when mature. The fruit are 3-4 cm across. Trees may bear thousands of fruit which are eaten by birds. Named varieties occur based on the colour of the fruit. The fruit are edible.
A tropical plant. They occur in the Philippines in lower forested regions from Luzon to the provinces of Mindanao. In Australia they are in the tropical rainforests and in coastal districts. Trees demand humidity and light. They are often on well drained soils at the edge of the rainforest. It grows in valleys at low and middle altitudes in S China. In Indonesia trees grow up to 1,500 m altitude. In XTBG Yunnan.
Common Names: Variegated Fig, Ara kelepong, Ara kelumpong, Ayak, Common red-stem fig, Ghundhang, Gondang, Kanjilu, Kara, Kendang, Kelo, Kondang, Ngoa rung, Nyawai, Phuuk, Pohon ara merabiasa, Tandilan, Tangisang-bayauak, Tentabau, Va rung, Za se rong
Synonyms:
Covellia racemifera (Roxb.) Miq.;
Ficus agusanensis Elmer;
Ficus amboinensis Kostel.;
Ficus cerifera Blume ex Bleekrode;
Ficus ceriflua Jungh.;
Ficus chlorocarpa Benth.;
Ficus compressitora Elmer;
Ficus cordifolia Blume;
Ficus ehretioides F.Muell. ex Benth.;
Ficus garciae Elmer;
Ficus glochidiifolia Hayata;
Ficus gummiflua (Miq.) Miq. ex Jungh.;
Ficus ilangoides Elmer;
Ficus integrifolia Elmer;
Ficus konishii Hayata;
Ficus laevigata Blanco;
Ficus latsoni Elmer;
Ficus paucinervia Merr.;
Ficus polysyce Ridl.;
Ficus racemifera Roxb.;
Ficus subopaca Miq.;
Ficus subracemosa Blume;
Ficus sum Gagnep.;
Ficus sycomoroides Miq.;
Ficus tenimbrensis S. Moore;
Ficus variegata var. chlorocarpa (Benth.) King;
Ficus variegata var. garciae (Elmer) Corner;
Ficus variegata var. ilangoides (Elmer) Corner;
Ficus variegata var. paucinervia (Merr.) Sata;
Ficus variegata var. pilosior Miq.;
Ficus variegata var. rotundata Sata;
Ficus variegata var. sycomoroides (Miq.) Corner;
Ficus viridicarpa Corner;
Sycomorus capensis forma tropica Miq.;
Sycomorus gummiflua Miq.;
Urostigma javanicum Miq.;
Ficus vasculosa
Edible: Leaves, Vegetable
A fig. It is a tree. It grows 15-44 m tall. The stem has white sap. The leaves are alternate and simple. The fruit are 8 mm across. They are round and on the twigs.
It is a tropical plant. It grows in rain forest up to 1,400 m above sea level. It grows on sandy soils. In XTBG Yunnan.
Common Names: Sweet mountain greens, Vasculosa fig tree, Pahugai, Pak de gai, Pohon ara vaskula, Shan tian cai, Tu mai rong
Synonyms:
Ficus championii Benth.;
Ficus renitens Miq.;
Ficus variabilis Miq.;
Ficus variabilis var. integrifolia Miq.;
Ficus vasculosa var. acuminata Miq.;
Ficus virens
Edible: Fruit, Leaves
A fig. It is a tall and often very large tree. It can lose all or some of its leaves during the year. It grows 15-30 m high and spreads 15-40 m across. It is a widely spreading plant often with a rounded crown. It can have both strangling roots and aerial roots. The trunk is short and very thick. It has irregular flanges on it and buttresses. It can have a mass of prop roots. The bark is dark grey to brown. Young shoots are bright green. The leafy growth at the base of the leaf is sword shaped and 10 cm long. The leaf stalk is 2-5 cm long. The leaves are 6-15-20 cm long and 4-6 cm wide. They are oval or sword shaped and thin but leathery. They are dark green above but with pale veins and leaves are dull underneath. The male and female flowers occur in the one fig. The male flowers are few and near the opening. The fruit or figs are about 1 cm across. They are round and greenish white to brown with white or red dots. They are wrinkled on the surface. Varieties with different leaf shapes have been described.
It is a tropical plant. It grows in a range of locations including rocky outcrops and rainforest. It needs well drained soil. It can grow in dry and humid regions. It is damaged by frost. In China it grows between 300-2700 m altitude in S China. Melbourne Botanical gardens. It suits hardiness zones 10-12. In XTBG Yunnan. In Townsville Queens BG.
Common Names: White Fig, Banyan, Deciduous Fig, Aaw, Albayi, Amchar, Biguan Rong, Chakkila, Ge bpong yang, Gelong den, Hishi, Hpak-hi, Kabra, Labra, Lu huang ge shu, Neme adao, Niza bao, Nuo na zi, Nyaung-chin, Nyaung-gyin, Nyaung-shin, Pakar, Pakur, Pa luo, Payer, Pen-cap banyan, Phak lueat, Pilkhan, Putkal, Sour buds tree, Suan bao shu
Synonyms:
Ficus carolinensis Warb.;
Ficus cunninghamii (Miquel) Miquel;
Ficus infectoria Miq.;
Ficus infectoria Roxb. var. lambertiana King;
Ficus lacor Buch.-Ham.;
Ficus lucescens Blume;
Urostigma lambartiana Miq.;
and others
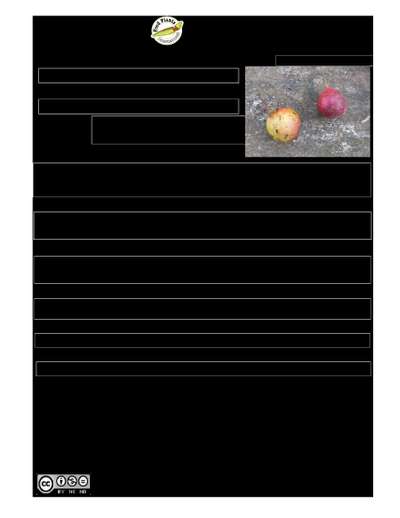
Flacourtia jangomas
Edible: Leaves, Fruit, Roots
A small deciduous tree up to 10 m tall. It spreads to 3 m across. The stem is erect and branching. Young tree parts can have large branched spines. The leaves are 5-10 cm long and 2-4 cm wide. Young leaves are red and glossy. There are several flushes of new growth during the year. Old trees often do not have thorns on the trunk or branches. Flowers are small and in clusters in the axils of leaves. They have a strong sweet smell. The fruit is a dull brownish red with a greenish yellow pulp. Fruit are about 2 cm across.
It is a tropical plant. It suits the hot humid tropical lowlands. In regions near the equator they are grown as a fruit tree up to about 600 m. They would probably grow up to about 1500 m altitude in the equatorial tropics. It also occurs wild. It can grow on almost any well drained soil. It does best in rich, moist soil. It needs a protected site and a partly shaded position. It is damaged by drought and frost. It suits hardiness zones 10-12. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Coffee plum, Baincha, Bainchakoli, Bo quan, Darichik, Finel, Goraji, Greater krekup, Heitroi, Hongquan, Indian plum, Jaggam, Jamuna, Kanji, Kareli, Kelukub, Kerekup, Kerkuh, Kerkup, Kerkup bakoh, Kerkup besar, Krakhob khmer, Kuragayi, Kyetyo-po, Lookloki, Lukluki, Mak-kyen, Malagache, Mu cuon, Mung quan rung, Mung quan, Muonquan, Naywe, Paiala, Painna gola, Paneli, Panial, Paniala, Peyala, Ponel, Ponial, Poniyol, Prunier malgache, Puneala plum, Rata-uguressa, Rukem, Runeala plum, Runealma, Sakhithei, Saralu, Sohmynloh, Sumbrung, Ta khopkhwai, Takop tai, Talisam, Talisapatramu, Talisha, Talispatra, Tambat, Tekroi, Thaislagondi, Thaislagunjul, Thengpe kondu, Umbuvah, Vayangarai, Vayankatha, Vhankali
Synonyms:
Flacourtia cataphracta Roxb ex Willd.;
Stigmarota jangomas Lour.;
Flacourtia rukam
Edible: Leaves, Fruit
A tree reaching a height of 5-20 m and about 30 cm across the trunk. It can be 40 m tall with a trunk 1 m across. The old branches are usually crooked with furrows along them. The leaves are 5 to 15 cm long and 4-7 cm wide and pointed at the tip. Young leaves are reddish brown and leaves are shiny on top. The young stems are very rough. The flowers are very small and occur in greenish yellow clusters in axils of leaves. They occur with separate sexes in separate flowers. The fruit is a flattened berry with soft juicy flesh and a red colour. The trunk in young trees has many simple spines. The leaf size and shape varies a lot.
A tropical plant. It grows in humid tropical conditions. It can grow in shade as well as full sun. They occur in Benguet to the southern parts of the islands of the Philippines. Trees occur in tall lowland rainforest. They probably grow from sea level up to about 1600 m in Papua New Guinea. In Samoa it grows from 50 to 550 m altitude. It suits hardiness zones 10-12. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Rukam, Aganas, Amaiit, Bitongol, Chemechong, Filimoto, Firmoto, Ganda rukem, Hong quan, Indian prune, Kalominga, Kaluminga, Ken, Khrop-dong, Klang tatah kutang, Kupa landak, Meptengkek, Mung guan ru'ung, Pohon rukem jambon, Rokam, Rukam bubur, Rukam gajah, Rukam manis, Rukem, Ta khop thai, Takho-thai, Tepetatah, Ukam
Synonyms:
Flacourtia edulis Griff.;
Flacourtia euphlebia Merr.;
Flacourtia megaphylla Ridl.;
Flacourtia peninsula Elm.;
Flacourtia rukam var. domestica Ridl.;
Flacourtia rukam var. erythrocarpa Ridl.;
Flacourtia rukam var. micronesica Fosberg & Sachet;
Flacourtia rukam var. myriantha Merr.;
Flacourtia sulcata Elm.;
Hisingera grandifolia Turcz.;
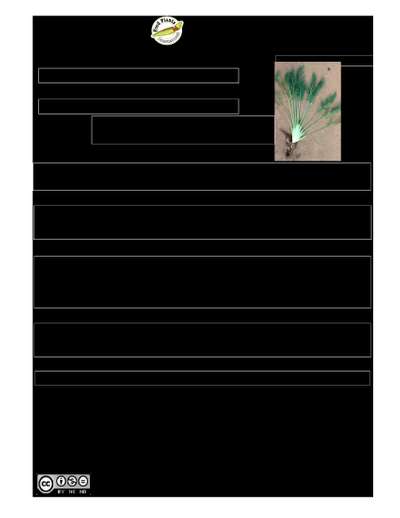
Foeniculum vulgare
Edible: Seeds, Leaves, Bulb, Herb, Spice, Vegetable, Oil, Roots, Flowers, Tea
A green leafy perennial herb. It can be 2 m high and 45 cm wide. The leaves are very fine. They have a feathery appearance. The stems are ribbed and at the bottom of the stalks there is a broad green section. When the leaves are crushed, they smell like aniseed. The flower at the top is a group of small yellow flowers. The seeds are oval and ribbed and about 5 mm long. Ripe fruit are wingless which distinguishes it from dill. There are several named cultivated varieties.
A temperate plant. It grows well in a Mediterranean climate. It grows well on dry and stony calcareous soils. It grows up to at least 2200 m altitude in the tropics. It grows better during the drier season at altitudes over 500 m. In PNG is grows between 1,400-2,200 m above sea level. It is cultivated but also easily grows wild. It is frost hardy. It grows in Nepal to about 2400 m altitude. In Argentina it grows from sea level to 1,000 m above sea level. It suits hardiness zones 5-10. Tasmania Herbarium. In Hobart Botanical gardens. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Fennel, Common fennel, Adas, Adeh manih, Arapcaci, Asi, Badishep, Badisopu, Besbas, Dereotu, Elbesbas, Fenchel, Fenneru, Fenocchio salvacce, Fenouil, Finocchio selvatico, Fonoll, Funcho, Hades, Hinojo, Hinojo amargo, Horom samit. Hui xiang, Jintan manis, Jira, Kagelanay, K'ama, Kokar ot, Komorac, Lebgoul, Madhurica, Maduru, Maraho, Masara, Masaro, Mauri, Millua, Morac, Mouri, Navadni komarček, Orla, Panmuhori, Peddajilakara, Phak chi, Rezene, Samon-saba, Samouk-saba, Saunf, Shamar, Shepu, Shombu, Shumar, Sonf, Sonp, Sopu, Sounp, Tseretso, Variari, Variyali, Vinkel, Wamssa, Yi ra, Yira
Synonyms:
Anethum dulce DC.;
Anethum foeniculum L.;
Anethum minus Gouan;
Anethum panmori Roxb.;
Anethum pannorium Roxburgh;
Anethum piperitum Ucria;
Anethum ruprestre Salisb.;
Foeniculum azoricum Mill.;
Foeniculum capillaceum Gilib.; [Invalid]
Foeniculum divaricatum Griseb.;
Foeniculum dulce Mill.;
Foeniculum officinale All..;
Foeniculum scoparium Quezel;
and others
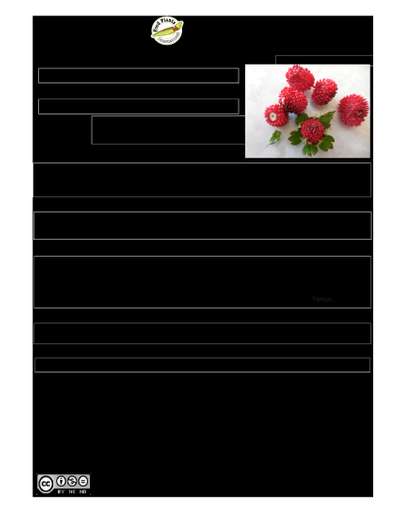
Fragaria chiloensis
Edible: Fruit, Leaves - tea
A small herb that keeps growing from year to year. The rootstocks are stout, thick and scaly. It grows 15 cm high and spreads 50 cm across. The fruit can be red, white or yellow. The leaves are short and thick and hairy underneath. The flowers are on long slender stalks. The flowers have 5 petals. The flowers are white. The fruit are red and edible. They can be 2-3 cm long.
A temperate plant. It grows naturally in coastal areas in cool locations. In Hawaii they grow between 1,200-2,000 m altitude. It suits hardiness zones 4-10. In Chile it grows from sea level to over 2,000 m altitude.
Common Names: Sand strawberry, Beach strawberry, Pine strawberry, Chilean strawberry, Dau-tay, Fresa, Frutilla, Frutilla silvestre, Ilahuen, Kellen, Pineapple strawberry, Quellen
Synonyns:
Fragaria vesca var. chiloensis L.;
Potentilla chiloensis (L.) Mabb.;
and others
Fragaria vesca
Edible: Fruit, Leaves - tea
A small plant which keeps growing from year to year. It grows to 20 cm high and spreads to 30 cm wide. The stems are long runners which form roots at the nodes. The leaves have 3 leaflets and are bright green. The leaflets are oval and with coarse teeth around the edge. They are 6 cm long and arranged in rings on long leaf stalks. The flowers are small white and open. They have 5 petals. The fruit are oval and fleshy. They are white and turn red (or white) as they ripen. They are sweet. A strawberry with small leaves and fruit and the seeds are on the outside of the fruit.
It is a temperate plant. It grows in the highlands in the tropics. It grows from 1600 m up to 3550 m in the tropics. They do poorly in hot humid climates. It becomes naturalised in high mountain regions in Papua New Guinea. It needs well drained soils and a protected sunny position. They are drought and frost tender. They enjoy acid soil. It suits hardiness zones 5-9. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
Common Names: Alpine strawberry, Woodland strawberry, Ameibuji, Bhui aselu, Bhuikaphal, Buti, Czerwone, Dag cilegi, Dau-tay, Divlja jagoda, Dreza, Erdei, Fodi eper, Fresa silvestre, Fragola, Fragula, Frutilla, Getnamori, Gorska yagoda, Jagoda sumska, Lulestrydhe, Maasikas, Maduixera, Maiore, Mandzoi, Mark-jordbaer, Marts'qvi, Maizi, Metsmaasikas, Meza zemenes, Navadni jagodnjak, Pahari rashberi, Paziemkos, Sa-mrep, Strawberi hutan, Wilde aardbei, Xia jiu, Yabani cilek, Zemlianika
Synonyms:
Fragaria insularis Rydb.;
Fragaria monophylla Duchesne;
Fragaria vesca var. monophylla (Duchesne) Ser.;
Potentilla vesca (L.) Scop.;
See Fragaria nubicola;