Two simple clothes washers are outlined in this Technical Bulletin.
The first, designed by VITA Volunteer Dale Fritz, consists of a covered galvanized metal tub, in which a long-handled agitator is plunged vigorously through the clothes. It was used successfully in Afghanistan.
The other washer is a more complicated wooden washing machine made and tested by the United States Department of Agriculture's Home Economics Laboratory in Beltsville, Maryland.
Both washers are easy to construct with readily available materials, and should help simplify washday chores.
Please send testing results, comments, suggestions and requests for further information to:
VITA 1600 Wilson Boulevard, Suite 500 Arlington, Virginia 22209 USA Tel: 703/276-1800 . Fax: 703/243-1865 Internet: pr-info@vita.org
ISBN 0-86619-093-7
VOLUNTEERS IN TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
VITA Technical Bulletins offer do-it-yourself technology information on a wide variety of subjects.
The Bulletins are idea generators intended not so much to provide a definitive answer as to guide the user's thinking and planning. Premises are sound and testing results are provided, if available.
Evaluations and comments based on each user's experience are requested. Results are incorporated into subsequent editions, thus providing additional guidelines for adaptation and use in a greater variety of conditions.
SIMPLE CLOTHES WASHER
Tools and Materials
Tinships
Pliers
Hammer
Soldering Equipment
Heavy galvanized sheet metal:
140cm x 70cm (55 1/8" x 27 9/16") for tub
100cm x 50cm (39 3/8" x 19 11/16" for lid and bottom
36cm x 18cm (14 3/16" x 7 1/16") for agitator
Wooden handle 140cm (55 1/8") long, about 4cm (1 1/2") in diameter
Rivets
Nails
Making the Washer
Figures 1 to 4 show how this washer is made. The tub, lid and agitator are
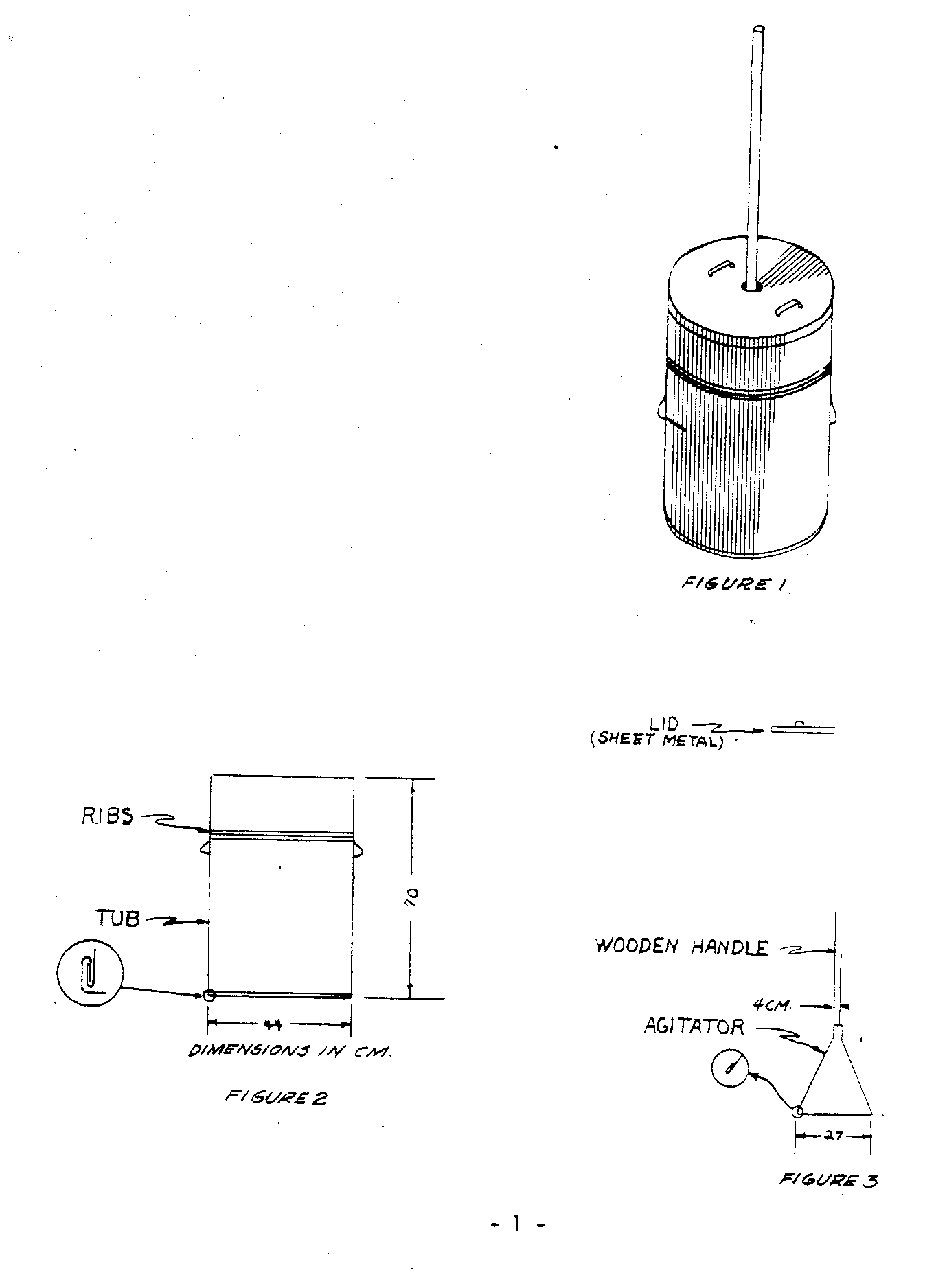
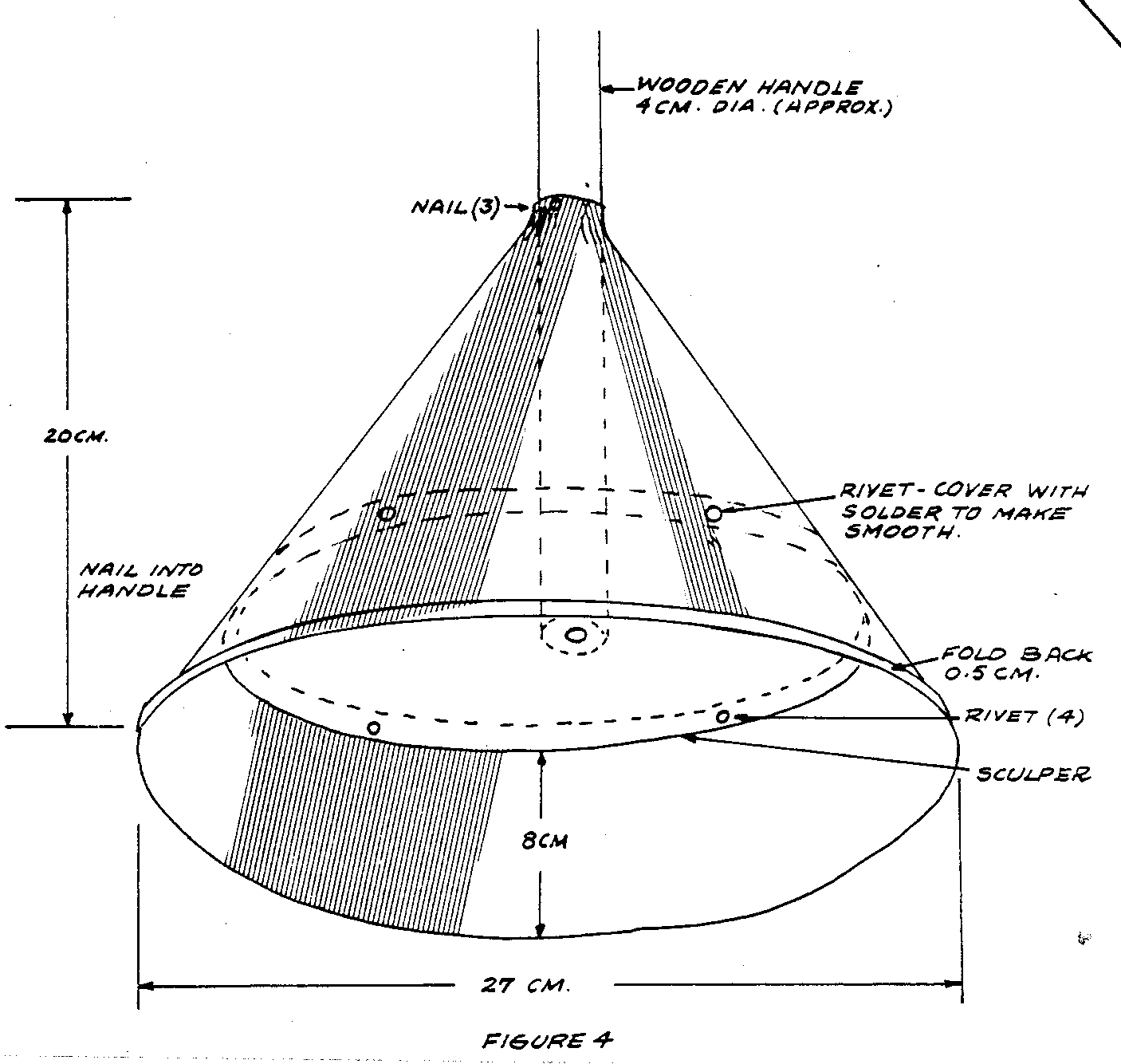

made of heavy galvanized sheet metal.
Using the Washer
To operate the washer, work the agitator up and down with a quick motion but with a slight pause between strokes. The movement of the water caused by the agitator will continue for a few seconds before additional agitation is needed. On the upward stroke the agitator should come completely out of the water. The agitator should not hit the bottom of the tub on the downward stroke because this would damage both the tub and the clothes.
HAND-OPERATED WASHING MACHINE
This easily operated washing machine can be built by a good carpenter from materials readily available in most countries. It is easy on clothes, effective and sanitary. The machine, which can take a 3-kilogram (6-pound) load of clothes, can be shared by several families.
Clothes will last much longer if they are washed in this washing machine rather than beaten or scrubbed on rocks. Washing with the machine is also much less work. A pilot model of the machine was made by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and tested in the USDA Home Economics Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Under test conditions, a comparison with standard electric commercial washers was very favorable. If the cost of the machine is too much for one family, it can be shared by several. However, if there are too many users, competition for times of use will become keen and the machine will wear faster.
Tools and Materials
Wood Parts:
Tub Construction - Moderately firm softwood (such as cedro of Latin America) free from large heartwood growth.
Sides - 2 pieces - 2.5 x 45.7 x 96.5cm 1" x 18" x 38"
Ends - 2 pieces - 2.5 x 30.5 x 40.6cm 1" x 12" x 16"
Bottom - 2 pieces - 2.5 x 15.2 x 40.6cm 1" x 6" x 16"
Bottom - 1 piece - 2.5 x 40.6 x 66.0cm 1" x 16" x 26"
Legs - 4 pieces - 2.5 x 10.2 x 76.2cm 1" x 4" x 30"
Round Plungers -
2 pieces - 2.5 x 25.4cm diameter 1" x 10" diameter
2 pieces - 3.8 x 12.7cm diameter 1.5" x 5" diameter
Cover (may be omitted)
2 pieces - 2.5 x 20.3 x 91.4cm 1" x 8" x 36"
6 pieces - 2.5 x 7.6 x 20.3cm 1" x 3" x 8"
Operating parts - Moderately firm hardwood such as Caoba of South America.
Lever
1 piece - 2.5 x 7.6 x 122cm long 1" x 3" x 48"
Plunger stems
2 pieces - 2.9cm square 38.1cm long 1 1/8" square 15" long
Uprights
2 pieces - 2.9 x 7.6 x 61.0cm long 1 1/8" x 3" x 24" long
Pivot and Handle
2 pieces - 3.2cm diameter x 45.7 cm long 1 1/4" diameter x 18" long
Metal Parts
Plunger connections -
4 pieces iron or brass plate - .64 x 3.8 x 15.2cm long 1/4" x 1 1/2" x 6" long
10 rods - 3.6 or .79cm diameter 1.4" or 5/16" diameter
45.7cm (18") long with threads and nuts on each end - iron or brass.
20 washers about 2.5cm (1") diameter with hole to fit rods.
1 rod - .64 x 15.2cm (1/4" x 6") with loop end for retaining pivot.
6 bolts - .64 x 5.1cm long (1/4" x 2" long)
24 screws - 4.4cm x #10 = flat head (1 3/4" x #10)
50 nails - 6.35cm (2 1/2")
Strip Sheet Metal with turned edge - 6.4cm wide, 152.4cm long (2 1/2" wide, 72" long)
Loose cotton or soft vegetable fiber for caulking seams.
Minimum Tools Needed
Tape measure or ruler
Saw
Screw Driver
Adjustable Wrench
Draw knife or plane and coping saw
Hammer
Wood chisel 1.3 or 1.9cm wide 1/2" or 3/4"
Pliers
0.64cm (1/4") drill, gimlet or similar tool
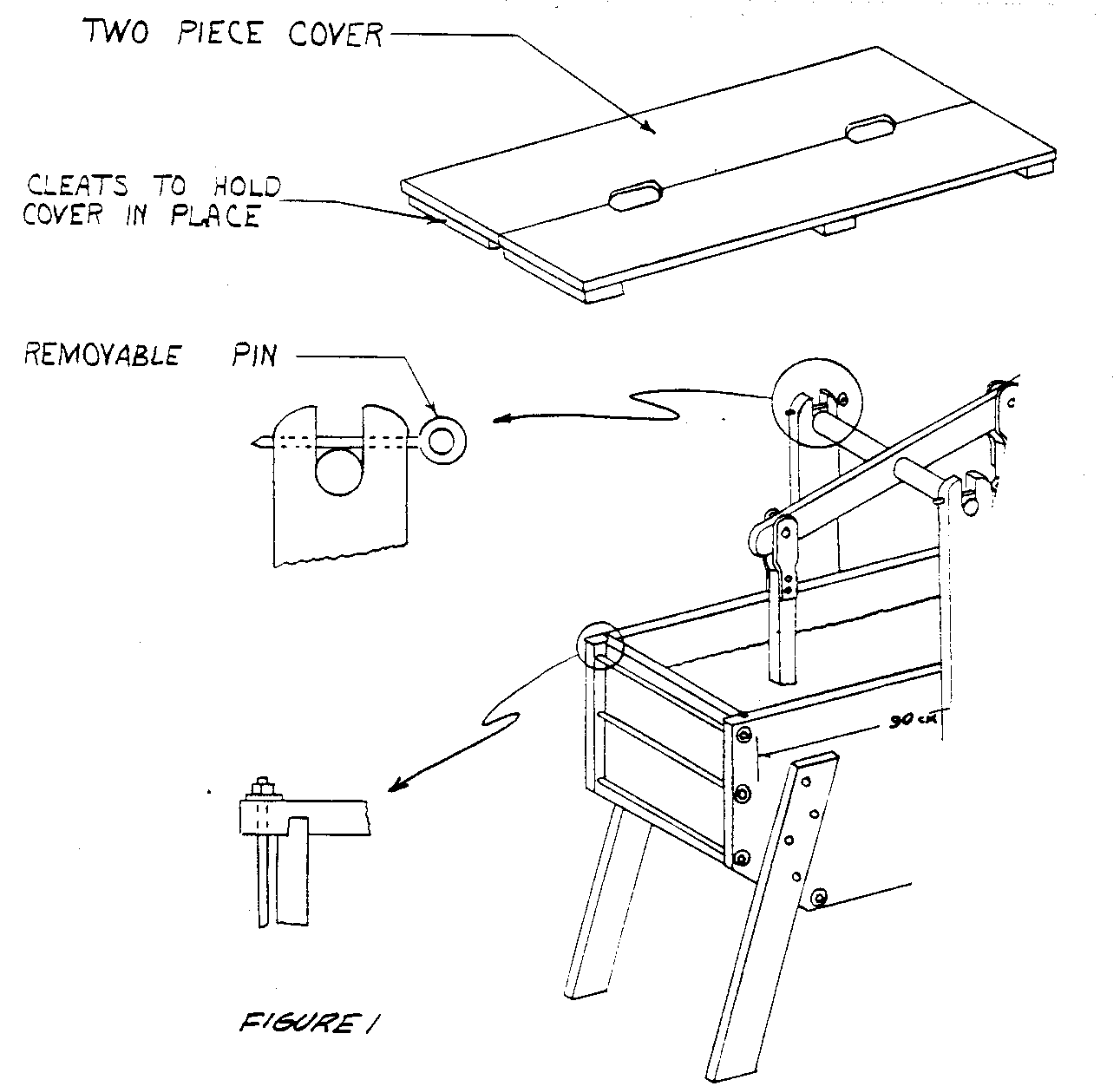
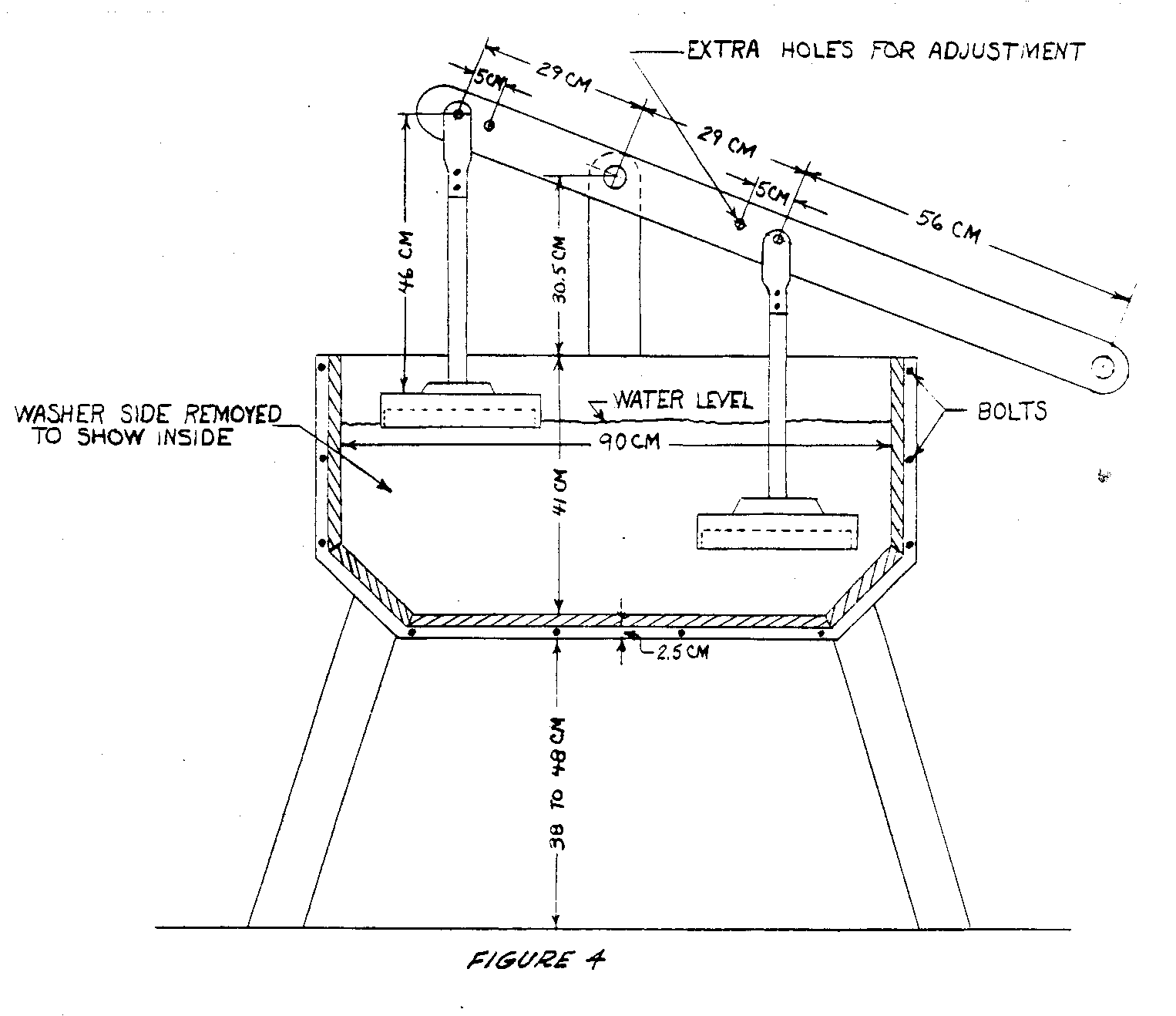
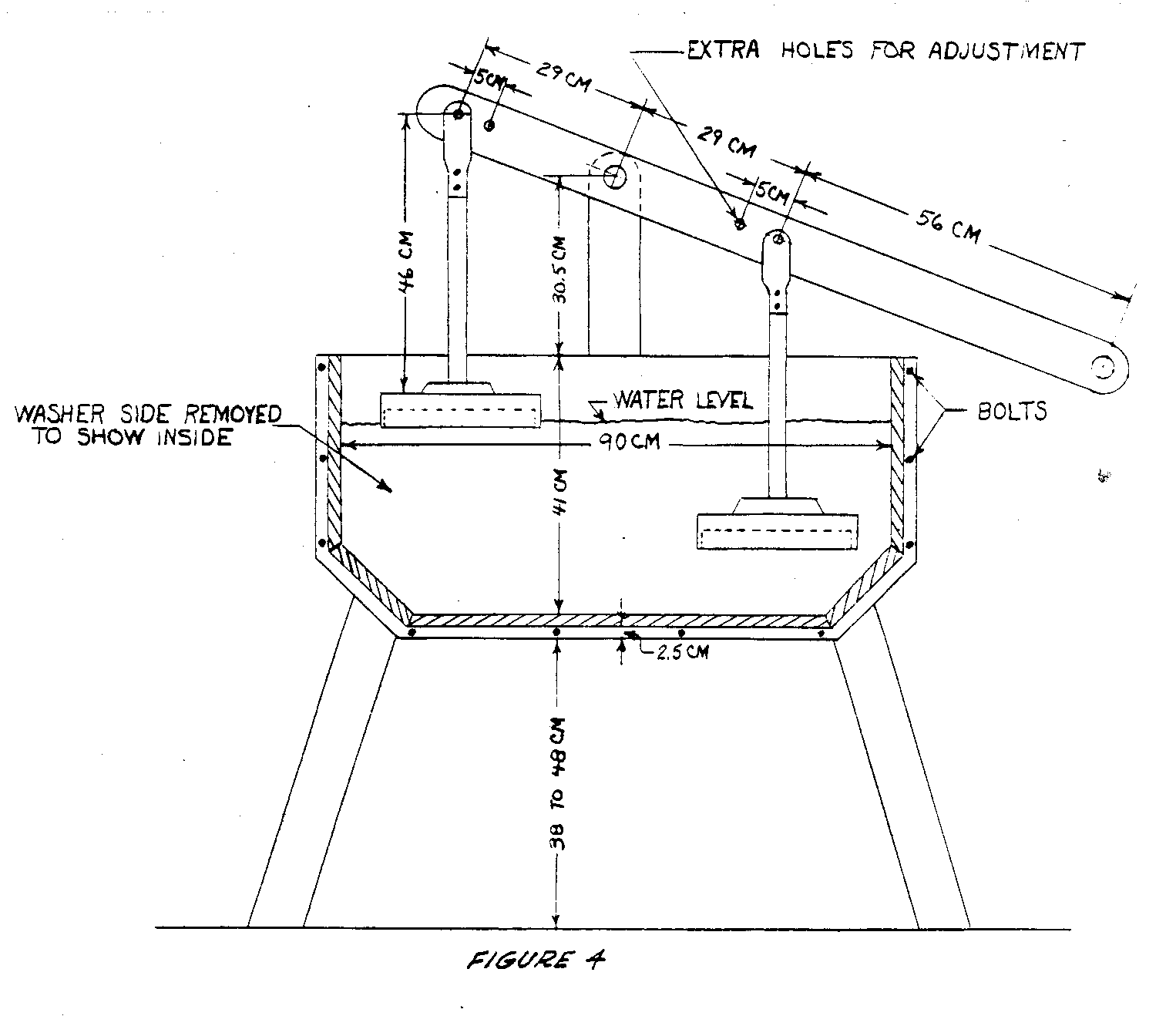
The machine reverses the principle used in the usual commercial washer, in which the clothes are swished through the water for various degrees of a circle until the water is moving, and then reversed. In this machine, the clothes stay more or less stationary while water is forced back and forth through them by the piston action of the plungers. One plunger creates suction as it rises and the other plunger creates pressure as it moves downward. The slopes at the ends of of the tub bottom help the churning action of the water caused by the plungers (see Figure 1).
A rectangular tub is best for this method of operation. This is fortunate since the rectangular box is easy to build. In general, any moderately strong wood that will not warp excessively (such as cedro in Latin America) will be satisfactory. The sides should be grooved for the ends and bottom of the tub as indicated in Figure 1 and bolted with threaded rods extending through both sides with washers to draw them tight. The bolting is necessary to prevent leaks.
The size described in the drawings is large enough for an average family in the U.S. The same principle may be used for a larger or smaller machine provided the basic proportions are maintained. Width of the tub should be slightly less than half its length to get a proper surge of water. The pistons should be wide enough to move within a couple of inches of each side of the tub. The lever pivot should be high enough to permit the plungers to move up and down several inches without the edge of the lever hitting the edge of the tub. Likewise, the length of the rods on the plungers must be such that the plungers go well into the water and the clothes come completely out of the water at the highest position.
- Mark and groove sides for end and bottom members (See Figures 1 and 4).
- Drill holes for cross bolts.
- Cut off corners and trim ends of side members to length.
- Bevel ends and bottom pieces to fit into groove in side members.
- Miter bottom and end members together.
- Assemble and bolt.
- Cut and install legs.
Caulk seams between ends and bottom members with loose cotton or other vegetable fiber to make seams water-tight. If joints to side members are carefully made, they may not need caulking.
Bore hole and make plug for draining tub. NOTE: This is shown on side in drawing but it is better in bottom of tub.
Make and install upright pivot members.
Make and install plunger lever. NOTE: The cross pivot member (round) should be shouldered or notched at each pivot to prevent side movement.
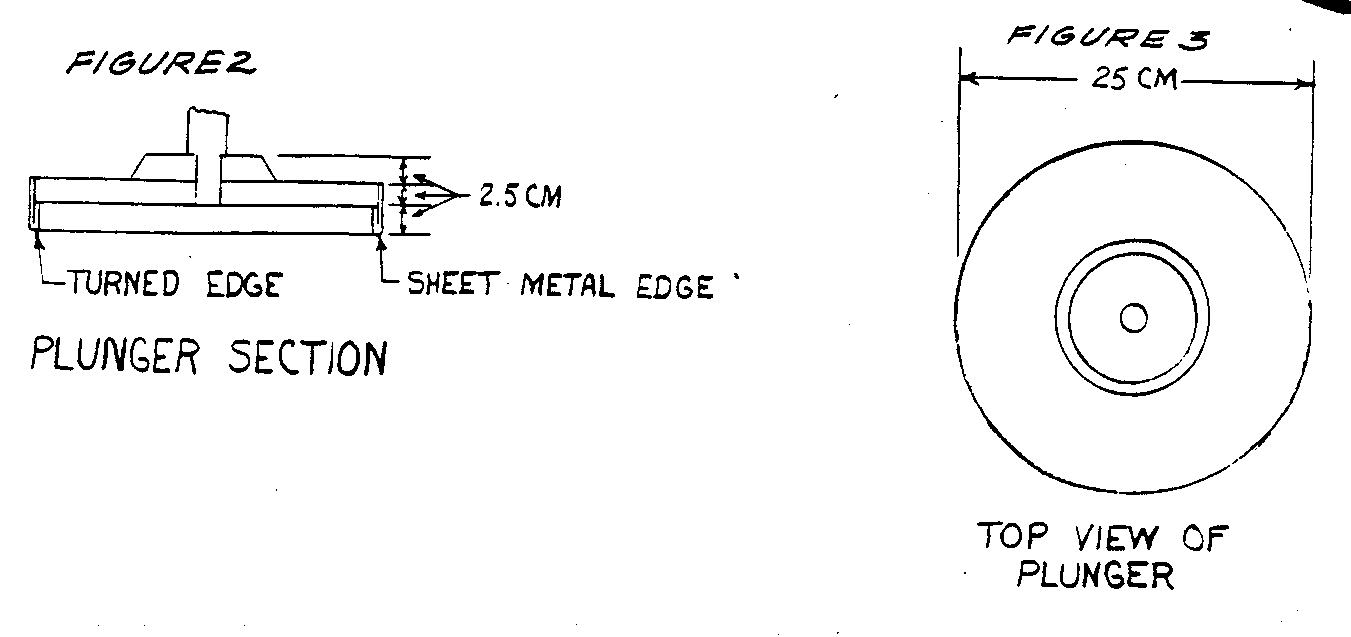
Make plungers and install (see Figures 2, 3 and 4).
Here are several suggestions for using this washing machine: fill the water with fifteen gallons of warm or hot water depending on what is available. Try to remove stains in clothing before putting it in the wash water. Rub soap into areas like cuffs and collars which come in close contact with the body. Soak very dirty clothes before putting them in the washer. Soap can be dissolved by shaving it into strips and then heating it in a small quantity of water before adding it to the wash water. A three kilogram load of clothes is the right size load for best cleaning. Wash at a moderate speed, about fifty strokes a minute, for ten minutes--longer if it seems necessary.
If more than one load of clothes is to be washed, some basic procedures will help to simplify the job and conserve water. (Water used for washing and rinsing can help to irrigate a garden plot.)
First divide the clothes so that whites and light colors are separate from dark clothes. Try to keep small items together so they won't get lost. Heavily soiled or greasy clothes should be washed alone.
Wash the white or light-colored things first in the hottest possible water (remember you will have to be able to handle the wet clothes--don't get the water too hot!), then move on through darker clothes. The water will become discolored. Much of the color is dirt, of course, but some is excess dye. The lightest clothes are washed in the cleanest water; dark clothes won't be as noticeably affected by the coloring matter in the water.
After each load, the wash water can be warmed if necessary by adding some boiling water. A bit more soap may also be needed. Probably at least three loads of clothes--depending on how dirty they are--can be washed before the water becomes too murky to be used again.
The clothes, of course, will have to be rinsed thoroughly. Soap or detergent residues can damage fabrics and may cause allergic reactions. A minimum of two rinses is usually necessary.
Probably the easiest (but most expensive) procedure is to have separate tubs for rinsing. Tubs can be of either wood or galvanized metal, and may be used for other purposes provided they are cleaned thoroughly on wash day.
When clothes are clean, squeeze out as much excess water as possible and put them into the rinse water. The next load of wash can be soaking while the first is rinsed and put to dry. Then the clothes in the machine are washed and the process repeated.
If no separate rinse tubs are available, wash up to three loads (if the water stays clean enough that long) and set each aside. Be sure to keep loads separate, as dyes from wet clothes may stain lighter colored fabrics. Then drain and rinse the washing machine and refill it with clean water. Rinse the clothes, again starting with the lightest colored load, and put out to dry. Repeat the whole wash-rinse process as often as necessary.
Another method is to wash the first load of clothes and squeeze out excess water. Drain the wash water and refill the machine with clean warm water. Rinse the clothes, squeeze out excess water, and put out to dry. Warm the rinse water with boiling water and add some soap. Then wash the next load. Repeat the procedure as often as necessary.
After washing and rinsing the clothes, rinse the washer clean and then replace the stopper. To keep the wood from drying out and causing the tub to leak, put about 3cm of water in the washer when it is not in use.
VITA
VOLUNTEERS IN TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
ABOUT VITA
Volunteers in Technical Assistance (VITA) is a private, nonprofit, international development organization. Started in 1959 by a group of concerned scientists and engineers, VITA maintains an extensive documentation center and worldwide roster of volunteer technical experts. VITA makes available to individuals and groups in developing countries a variety of information and technical resources aimed at fostering self-sufficiency--needs assessment and program development support; by-mail and on-site consulting services; information systems training. It also publishes a quarterly newsletter and a variety of technical manuals and bulletins.
VITA 1600 Wilson Boulevard, Suite 500 Arlington, Virginia 22209 USA Tel: 703/276-1800 . Fax: 703/243-1865 Internet: pr-info@vita.org