Some 3 billion people in the world live outside the cash economy in the world’s poorest nations. Food security and regular supply are their daily concerns. Chronic malnutrition is a leading cause of death and disease for them. Young children are amongst the most affected. One child every 5-10 seconds dies from undernutrition. Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness for someone every minute. Most people in tropical and subtropical countries are iron deficient.
Our goal is to provide information that enables people to choose the right plant for their environment, to give them stable food production and a greater choice of plants to enrich their diets and improve their nutritional wellbeing.
The plant fact sheets listed in this collection are only a small portion of those available from FPI. Please check your plant inquiries in the ECHO Search and reference the FPI plant database for further information.
Most of the plants selected to list here are further described in country-specific publications by Food Plant Solutions (FPS in the Search).
8000 Starchy Staples
7000 Legumes
6000 Leafy Greens
5000 Fruits
4000 Vegetables
3000 Nuts, Seeds, Herbs, and other foods
948 Contenido (Mostrando Ediciones - ) Anterior | Próximo
Blechnum orientale
Edible: Rhizome, Root, Fronds, Leaves, Vegetable
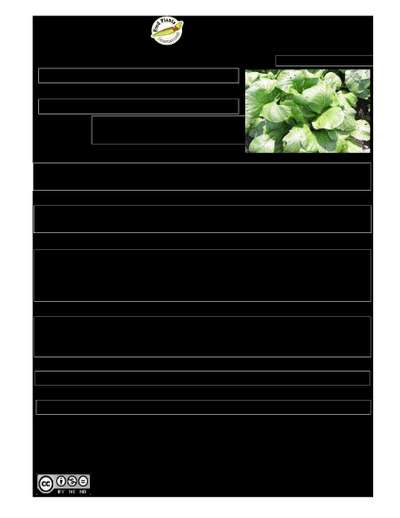
A medium to tall fern. It grows 0.3-1.2 m tall. It forms round clumps. The stem is short and has brown scales with very small teeth. The fronds can be 1 m high. The fronds are spreading or erect, forming a rosette. They often droop at the tips. The side leaflets are thin and long, with a long pointed tip. They do not have teeth along the edge. They are about 20-25 cm long and 0.8-1.8 cm wide. They are attached directly to the stalk. The youngest leaflets are pink. The leaf segments are rounded and smallest at the base. The fronds are dark green and shiny. The spore bodies are produced under the fertile fronds which have an appearance similar to the other fronds. These spores occur in a long continuous line along both sides of the midrib.
A tropical plant. It occurs in rainforest and swampy areas. It suits humid locations. It grows best with regular water but can tolerate some sun and dryness. It grows in forest clearings and along roadsides. It is frost tender. It can grow on rocky edges of waterfalls. In China it grows between 200-1,000 m above sea level. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Bungwall, Mountain fern cat, Centipede fern, Dhekiashak, Dheki shak, Ge long, Haththazori, Julia roroa, Khammouan, Mahrekenleng, Majuwa, Paku jahe, Paku kelindang, Paku lipan, Paku lobang, Parangipang, Rang dua dong, Vawm-ban, Vomban
Synonyms:
Blechnopsis orientalis (L.) C. Presl.;
Blechnum javanicum Blume;
Blumea balsamifera
Edible: Leaves, Leaves - seasoning
A small herb. It grows to 3 m tall. It is short lived. The bark is yellow-brown. The branches and leaves have a silky covering. The leaves are about 7-25 cm long by 3-10 cm wide. The flowers are in small heads. The flowers are yellow. The fruit are ribbed.
A tropical plant. It grows in forest. It can also grow in desert soils. It can grow in arid places. At MARDI. In XTBG Yunnan.
Common Names: Ngai camphor plant, Buffalo ear, Bunga sapa, Chapa, Chapor, Galunggung, Hhaoqsaqlagma Yaoheeqjaiq, Kakaronda, Kakrondra, Kam pawng, Kaphur goch, Na dyai, Na luang, Phak naad, Phon-ma-thien, Sembang, Sembing, Semboh, Sembong
Synonyms:
Conyza balsamifera L.;
Blumea lacera
Edible: Leaves
A herb which keeps growing each year. It can grow each year from seeds. It can be 20 cm to 2.5 m. The stems are hairy. They are erect and stiff and brittle. They have a woody rootstock and often grows to 1 m tall. There are many branches. The leaves are produced one after the other on opposite sides of the stem. They are hairy on both surfaces. There are irregular teeth along the edge of the leaf. The flowers develop at the top of the plant. The fruit are brown and with ribs and about 1 mm long.
A tropical plant. In Papua New Guinea it occurs between 100 and 2,000 m altitude. It Java it grows to 1,500 m above sea level. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
Common Names: Kakronda, Malay blumea, Anra mang, Batu linchar, Bugi, Burando, Cai ma, Cai triu, Gangrima, Kakradna, Kayu batu, Khicha bhwatha, Kopile jhar, Kukuradru, Kukursunga, Kurkure, Lalangkapan, Lumai hutan, Mugongreng, Peau, Sembung lalaki
Synonyms:
Baccharis auriculata Wall. ex DC.;
Blumea bodinieri Vaniot;
Blumea cernua DC.;
Blumea cinerascens DC;
Blumea commersonii Edgew.;
Blumea cuneifolia DC.;
Blumea dregeana DC.;
Blumea elongata DC.;
Blumea fontinalis Edgew.;
Blumea glandulosa DC.;
Blumea heyneana DC.;
Blumea hieraciifolia Hook. f. & Thomson;
Blumea holosericea DC.;
Blumea hymenophylla DC.;
Blumea lacera var. (several);
Blumea musra DC.;
Blumea subcapitata DC;
Blumea thyrsoidea Sch.Bip.;
Blumea trigona DC.;
Blumea velutina H. Lev. & Vaniot;
Blumea villosa Sch.Bip. ex Hook. f.;
Conyza amoena Link;
Conyza dentata Blanco;
Conyza hamiltonii Steud.;
Conyza lacera Burm.f.;
Conyza lactucifolia (DC.);
Conyza natans Buch.-Ham. ex Hook.f.;
Conyza necessaria Buch.-Ham. ex DC.;
Conyza runcinata Wallich; ?
Conyza subcapitata Wallich; ?
Conyza thyrsoidea Pers.;
Conyza velutina (H. Lev. & Vaniot) H. Lev.;
Erigeron exstipulatus Dchumach. & Thonn.;
Senecio velutinus H. Lev. & Vaniot;
Boehmeria nivea
Edible: Root, Leaves, Seeds - oil, Flowers, Stem
An erect shrub which grows from year to year. It is 1-3 m tall. The underground roots are thick storage roots. The leaves occur one after another along opposite sides of the stem. The leaves have long leaf stalks and are oval but broad. They have teeth along the edge. They are 7.5-15 cm long by 5-10 cm wide. The leaves are white underneath. The more tropical form does not have hairs under the leaf. The flowers are small. They occur in the axils of leaves. The flowers have separate sexes. The male flowers are lower down and the female flowers higher up. The fruit is a small dry one seeded fruit. It is brownish-yellow and about 1 mm long. Flowers are wind pollinated.
A tropical and subtropical plant. The plant grows best in warm moist climates. It needs rich well drained soil. It can grow in part shade. It grows on the edges of forests between 200-1,700 m above sea level. Melbourne Botanical gardens. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
Common Names: Ramie, Ban, Bela kopriva, China Grass, Gon, Kankura, Kya-sha, Lashen, Rami, Rhea
Synonyms:
Boehmeria tenacissima Gaudich.
Boesenbergia rotunda
Edible: Rhizome, Root, Tubers, Leaves, Spice
A part of the ginger family. The plant continues to grow from year to year. The plant is 30-50 cm high. The roots are like a long orange brown group of fingers. These rhizomes are the size of fingers. They are 6-10 cm long and 1 cm wide. Inside the brown skin is a yellow sweet smelling tissue. The leaves occur as 3-4 leaves 10-30-50 cm long by 5-10 cm wide. The leaf stalk is 5-12 cm long and has a channel. The leaf sheath is red. The flowers are at the ends of the stalk. There are few flowers surrounded by narrow bracts. Each bract 5 cm long surrounds one flower. The flowers are white or pink. The flowers have a smell. The fruit is oval.
It is a tropical plant. In colder regions, leaves will die back in winter. They need a fertile, open, loamy soil. The soil need to be well drained. They shoot best with warmth and humidity. They then grow best in warm shady positions. They need a rainfall of 1000 mm per year. In China it grows in dense forests at about 1000 m in S China. In Cairns Botanical Gardens.
Common Names: Chinese keys, Ardong, Bhuchampakamu, Bhuichampa, Chee-puu, Chinese ginger, Dekunchi, Finger root ginger, Kachai, Khchiey, Kondakalava, Kra chaai, Krachai, Kunci, Kunir putih, Merkunchi, Poh-see, Seik-phoo, Suo shi, Temoo kuntji, Temu kechil, Temu kunchi, Temu kunci, Temu putri, Tiha, Tihaso, Yai macha
Synonyms:
Boesenbergia cochinchinensis (Gagnep.) Loes.;
Boesenbergia pandurata (Roxb.) Schlecht.;
Curcuma rotunda L.;
Gastrochilus panduratus (Roxb.) Ridley;
Gastrochilus rotundus (L.) Alston;
Kaempferia cochinchinensis Gagnep.;
Kaempferia ovata Roscoe;
Kaempferia pandurata Roxb.;
Bombax ceiba
Edible: Roots, Leaves, Flowers, Fruit, Seeds, Seeds - oil, Gum
A large tree. It loses its leaves in the dry season. It grows to 20-25 m tall and spreads to 8-15 m wide. The stem is erect. It has buttresses when mature. The trunk and branches are covered with large pyramid shaped spines. The crown is umbrella shaped. The bark is pale ash coloured. It develops cracks along its length with age. The leaves are arranged like fingers on a hand. The leaves are rounded and 30-50 cm across. There are 5-7 leaflets which are elliptical. These are 12-20 cm long. The leaves are bright green and leathery. The trees flower during the dry season when the tree has no leaves. The flowers are red, open or cup shaped and 10-15 cm across. The flowers are often clustered near the ends of branches. The flowers appear while the leaves have fallen from the tree. The flower petals are thickened and curved backwards in the upper half. The fruit is a brown oval capsule. This seed envelope is about 15 cm long. It has 5 angles and many seeds. The seeds are covered with soft, silky cotton.
A tropical plant. It grows in tropical monsoonal rainforest. It suits humid locations. It requires an open sunny position. It will grows on most soils. It can grow in limestone areas. It is drought and frost tender. Trees must have a temperature above 13°C. In Nepal plants grow to 1200 m altitude. In the Indian Himalayas it grows between 1,200-1,400 m above sea level. They are found at low altitudes throughout the Philippines. In India they grow in all deciduous forests. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 10-12. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
Common Names: Kapok tree, Red silk-cotton tree, Boichu, Bombax, Booruga, Boorunga, Bouro, Bula, Buroh, Doak-ngew, Edel daru, Edelsong, Gao rung, Gon rung, Guan niu, Hambo, Illavam, Kaanti-senbal, Kadung, Kantakadruma, Kantesavar, Kate savar, Katesawar, Kawl-tung-peng, Kempu-booruga, Kempuburuga, Koki, Kroik, Leptan, Letpan, Mai-nio, Malabulak, Moc mien, Mu mian, Mulilavu, Mullelava, Mullila-pula, Mullilavau, Mullilavu, Mullubooruga, Mu mian yang, Neibie, Ngiew, Ngiu deng, Ngiu pa, Nglo, Ntoo yaj huab, Nuoliu, Pagun, Pan-ya, Panchu, Pemagesar, Pemguyser, Phakong, Pharkong, Pohon kapuk merah, Poola, Pula-maram, Pulai, Rakta-pushpa, Red Silk Cotton tree, Ro-ka, Roktosimul, Salmali, Samar, Samro, Sanar, Saur, Savar, Savri, Sawar, Semal, Semale, Sémul, Senur, Shaimbal, Shembal, Shemolo, Shevari, Shevri, Shimla, Shimul cotton, Simal, Simalo, Simalu, Simbal, Simla, Simlo, Simolu, Simuli, Singi, Syamling, Yi ka bu duo si
Synonyms: Bombax aculeatum L.;
Bombax ceiba var. leiocarpum Robyns;
Bombax malabaricum DC.;
Bombax heptaphyllum Cav.;
Salmalia malabarica (DC.) Schott & Endl.;
Gossampinus malabarica (DC.) Merrill;
Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis
Edible: Leaves, Stem, Flowers, Vegetable
A leafy cabbage grown as an annual. It grows 40-60 cm high. The taproot is not fleshy. The stem is short. The leaves are arranged in spirals. They are simple and broadly oval. They can be 30 cm long by 10 cm wide. The leaves form a rosette. They do not form a head. The leaf stalk is thickened. It forms a half cylinder in cross section and does not have wings. The leaf blade is entire and can have a wavy edge. Flowers are small and yellow with 4 petals. The fruit is a pod 3.5 cm long. The seeds are black and 2 mm long. Several different kinds occur.
A tropical plant. More common in lowland areas but will grow in the highlands. It suits cool seasons but will not tolerate frost. In PNG it grows between sea level and 2,300 m above sea level.
Common Names: Bok-choy Celery cabbage, Broad-beak mustard, Caisin, Celery mustard, Chinese cabbage, Chinese mustard, Chinese savoy, Chinese white cabbage, Choi sum, False pak-choi, Flat cabbage, Flowering white cabbage, Kisaragina, Mock pak-choi, Mustard cabbage, Pak choy, Ramirebaka, Ramiriba, Taatsai, Tah Tsai, Te kabiti n Tiaina, Tsoi sum, Yow choy
Synonyms:
Brassica chinensis Linnaeus;
Brassica antiquorum H. Léveillé;
Brassica campestris Linnaeus subsp. chinensis (Linnaeus) Makino;
Brassica campestris subsp. chinensis var. amplexicaulis (Tanaka & Ono) Makino;
Brassica campestris subsp. narinosa (L. H. Bailey) G. Olsson;
Brassica campestris var. chinensis (Linnaeus) T. Itô;
Brassica campestris var. narinosa (L. H. Bailey) Kitamura;
Brassica campestris var. parachinensis (L. H. Bailey) Makino;
Brassica chinensis var. communis M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica chinensis var. parachinensis (L. H. Bailey) Sinskaya;
Brassica chinensis var. rosularis M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica napus Linnaeus var. chinensis (Linnaeus) O. E. Schulz;
Brassica narinosa L. H. Bailey;
Brassica oleracea var. tsiekentsiensis H. Léveillé;
Brassica para-chinensis L. H. Bailey;
Brassica oleracea Linnaeus var. chinensis (Linnaeus) Prain;
Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis (Linnaeus) Hanelt;
Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis var. parachinensis (L. H. Bailey) Hanelt;
Brassica rapa subsp. narinosa (L. H. Bailey) Hanelt;
Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis var. rosularis (M. Tsen & S. H. Lee) Hanelt;
Brassica rapa var. amplexicaulis Tanaka & Ono;
Raphanus chinensis (Linnaeus) Crantz (1769), not Miller (1768);
Brassica juncea
Edible: Leaves, Seeds - oil, Spice, Vegetable, Flowers
It is an erect leafy annual cabbage plant. It grows to about 1 m high. The plant can vary a lot. The leaves are elliptical and deeply divided. They are dark green. The end segment of the leaves is oval. The leaves taper towards the stem and have a strong mustard flavour. The flowers are pale yellow. They have 4 petals. It produces a flower and seed pods at the top. The seed pod is long and narrow. It is 3-5 cm long. The seeds are reddish-brown.
A warm temperate plant. It is grown in some highland areas in the tropics. It is often grown as a cool season crop. Most varieties are not frost tolerant. It needs a fertile, well drained soil. A pH of 5.5-6.8 is suitable. It can tolerate poor soils. In the Himalayas in summer it grows to 3,600 m altitude. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 9-11. Tasmania Herbarium. In Yunnan.
Common Names: Indian mustard, Leaf mustard, Chinese mustard, Acelga china, A-mothsora, Ananatsongo, Antam, Brown mustard, Cai be-xanh, Cai canh, Dijon mustard, Dongi, Figiri, Gai choi, Jie cai, Kaad khiew, Kaai ts'oi, Kabej-plasas, Kadugu, Kai choy, Karamkala, Kanganje, Karashi-na, Khat naa, Mbumbi, Modo metan, Monnyin-no, Mosita, Mostaza china, Mpatu, Mpiru, Mustasa, Nkofi, Phakkat-khieo, Phakkat-khieopli, Rai, Rai sorisha, Samon-ni, Sarepta mustard, Sawi, Sawi pahit, Se-sawi
Synonyms:
Brassica argyi H. Léveillé;
Brassica cernua (Thunberg) F. B. Forbes & Hemsley;
Brassica integrifolia (West) O. E. Schulz;
Brassica japonica (Thunberg) Siebold ex Miquel;
Brassica juncea subsp. integrifolia (West) Thellung;
Brassica juncea var. crispifolia L. H. Bailey;
Brassica juncea var. foliosa L. H. Bailey;
Brassica juncea var. gracilis M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica juncea var. integrifolia (Stokes) Sinskaya;
Brassica juncea var. japonica (Thunberg) L. H. Bailey;
Brassica juncea var. longidens L. H. Bailey;
Brassica juncea var. longipes M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica juncea var. multisecta L. H. Bailey;
Brassica juncea var. multiceps M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica juncea var. rugosa (Rox-burgh) Kitamura;
Brassica juncea var. strumata M. Tsen & S. H. Lee;
Brassica juncea var. subintegrifolia Sinskaya;
Brassica lanceolata (de Candolle) Lange;
Brassica napiformis (Paillieux & Bois) L. H. Bailey var. multisecta (L. H. Bailey) A. I. Baranov;
Brassica rugosa (Rox-burgh) L. H. Bailey;
Brassica taquetii H. Léveillé;
Brassica willdenowii Boissier;
Raphanus junceus (Linnaeus) Crantz;
Sinapis cernua Thunberg;
Sinapis chinensis Linnaeus var. integrifolia Stokes;
Sinapis cuneifolia Roxburgh;
Sinapis integrifolia West;
Sinapis japonica Thunberg;
Sinapis juncea Linnaeus;
Sinapis lanceolata de Candolle;
Sinapis patens Roxburgh;
Sinapis ramosa Roxburgh;
Sinapis rugosa Roxburgh;
Brassica nigra
Edible: Leaves, Seeds, Herb, Spice, Flowers, Vegetable, Oil
A cabbage family herb. It is an annual plant. It grows about 1-3 m high. The leaves are stalked and clasp the stem. The upper leaves are sword shaped. Leaves are 10-20 cm long. Flowers are yellow. The fruit is a pod. It is erect, smooth and 2 cm long. It can have 3-5 seeds. The seeds are reddish-brown to almost black. They are 1.5 mm across.
It is a temperate and Mediterranean climate plant. In China it grows on slopes, steppe, field margins between 900–2800 m altitude. In Nepal it grows to 2000 m altitude. In Ethiopia it grows between 1,500-2,600 m above sea level. Tasmania Herbarium.
Common Names: Black mustard, Ankam, Asnab, Cavuliceddu niuru, Crn sinap, Crna zelka, Esek turpu, Franciamustar, Gan-aba, Hardala, Hot-cai den, Huoirruoi, Kadugu, Kalo sorisha, Kalo tori, Kalu aba, Karahardal, Kerkaz, Mazzaredda amara, Monnyin-net, Mostacilla, Mostarda negra, Mostaza negra, Nzeyicheu, Rama negra, Rayo, Saiso, Sarso, Senafich, Sinapi, True mustard, Yaolaisa gisim
Synonyms:
Sinapis nigra Linnaeus;
Sisymbrium nigrum (Linnaeus) Prantl.;
many others
Brassica oleracea var. botrytis
Edible: Flowers, Leaves, Vegetable, Seeds sprouts
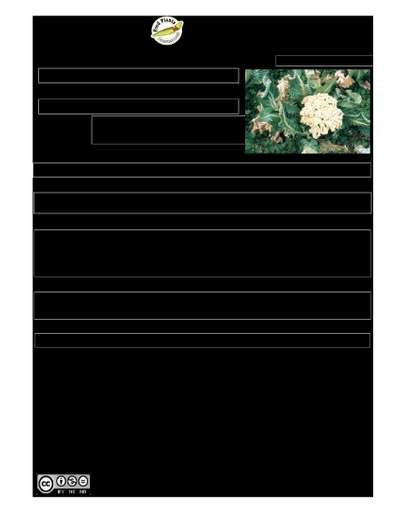
A herb. It is a cabbage family plant which develops a thick white edible flower in the centre. These can be yellow or purple. It has broad leaves around a thick stalk. The leaves clasp the stem. The leaves are oval and fleshy. The flowers are yellow.
It is a temperate plant. It mostly grows in the highlands in the tropics but has been grown from sea level to 2600 m altitude. In PNG it is best above 1,100 m above sea level. It is frost resistant. The best temperature is 14-21°C. In Nepal it grows up to 1800 m altitude. It suits hardiness zones 8-11.
Common Names: Cauliflower, Bloemkoolblad, Blumkol, Coliflor, Cvetača, Hua ye cai, Fulkopi, Kalam dok, Kalampii dook, Kaule, Kol bunga, Koli flawa, Kori, Kubis bunga, Monla-paw, Pan-kobi, Pan-mon-la, Parbawr, Phkaa spei, Phool ghoni, Phul-kopi, Sofilera, Thaba-paw, Ye ts'oi fa
Synonyms:
Brassica botrytis (L.) Miller;
Brassica cauliflora Garsault;